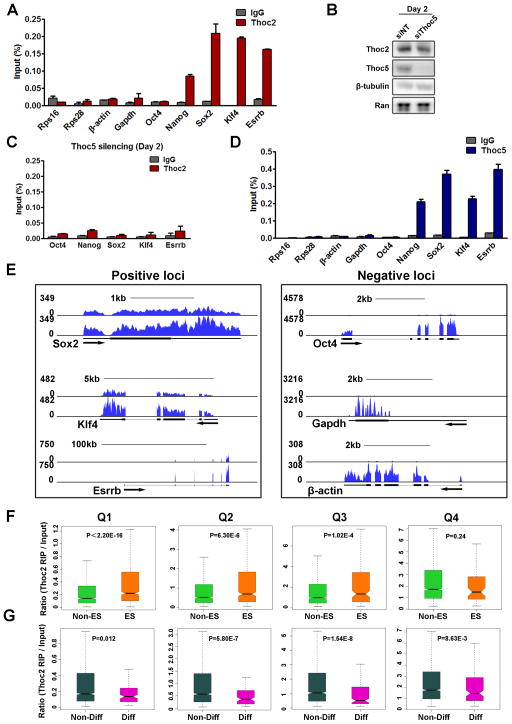
Figure 4. Thoc2 preferentially binds to pluripotency gene mRNAs in a Thoc5-dependent manner.
(A) Thoc2 interaction with mRNAs. RIP was performed in ESCs with either IgG or Thoc2 antibody. Relative abundance of the immunoprecipitated mRNAs was determined by RT-qPCRs and normalized to Input, and plotted as mean ± SEM from three independent experiments. (B) Thoc2 protein level 48 hours after Thoc5 silencing. (C) Effect of Thoc5 silencing on Thoc2 RIP. ESCs were transfected with Thoc5 siRNAs, and RIP was carried out 48 hours after transfection. Values are plotted as mean ± SEM. (D) Thoc5 interaction with mRNAs. RIP was performed in ESCs. Relative abundance of the immunoprecipitated mRNAs was determined by RT-qPCRs and normalized to Input, and plotted as mean ± SEM from three independent experiments. (E) Thoc2 RIP-sequencing. Thoc2 RIP was performed in ESCs, and the total and Thoc2-interacting RNAs were subjected to high-throughput sequencing. Representative images from the genome browser were shown for the indicated genes. (F–G) Statistical analysis of Thoc2 RIP-sequencing. Genes detected in the sequencing were ranked by their expression level in ESCs and divided into 4 equal groups (Q1–Q4). Thoc2 binding was determined by the ratio of the reads per kilo base per million (RPKM) in Thoc2 RIP/Input, and was compared between non-ES cell genes (Non-ES) and ES cell genes (ES) or non-differentiation (Non-Diff) and differentiation (Diff) genes in each quarter. ES genes were defined as those down-regulated during ESC differentiation, while differentiation genes were defined as those up-regulated (see methods for details). p-values were calculated by the Wilcoxon rank sum test.