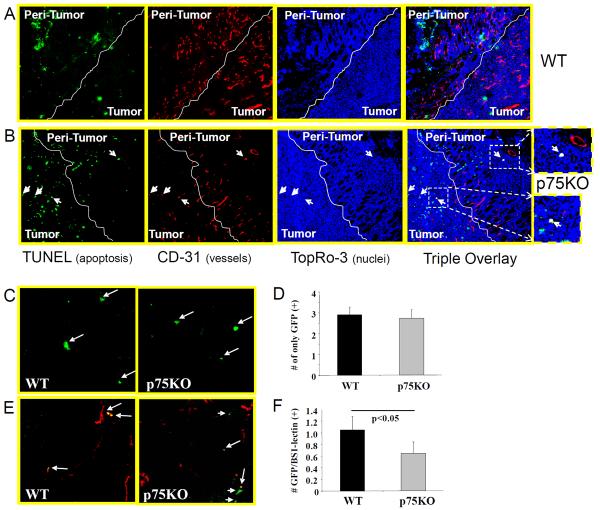
Figure 2. Increased apoptosis in tumors from p75KO mice at the border-zone and reduced incorporation of BM-derived EPCs into functional capillary network in p75KO tumors.
Apoptosis and tumor angiogenesis was also evaluated at the interface of tumor/normal tissue by triple staining with Terminal Transferase dUTP Nick End Labeling (TUNEL), CD31 and Topro-3. The peri-tumoral and tumor area was identified by H&E staining of adjacent sections (not shown). Representative images of triple-immunostained tumors (panel on the far right) in the periphery of tumor tissue for TUNEL (green), CD-31 (red) and Topro-3 (blue) in WT (A) and p75KO (B). A–B, TUNEL staining (top panel) in WT tumors. B, Insets in peri-tumoral (top) and tumors (bottom) in p75KOs show double positive (TUNEL/CD31-yellowish staining, arrowheads) indicating apoptosis of p75KO ECs. C, Representative images of BM-derived (GFP +) cells recruited into WT and p75KO tumor tissue (arrows). D, Quantification of BM-derived GFP (+) cells recruitment into the tumor tissue. E, Representative images of double BM-derived GFP (+)/BS-1/lectin (+) cells, incorporated into functional vessels (yellow staining, arrows). Small arrowheads indicate BM-derived GFP (+) cells that are not incorporated into functional vessels (green) in p75KO tumors. F, Quantification of BM-derived EPCs incorporation into the functional capillary network.