Figure 3. Effect of chronic ethanol on hippocampal [3H]8-OH-DPAT binding.
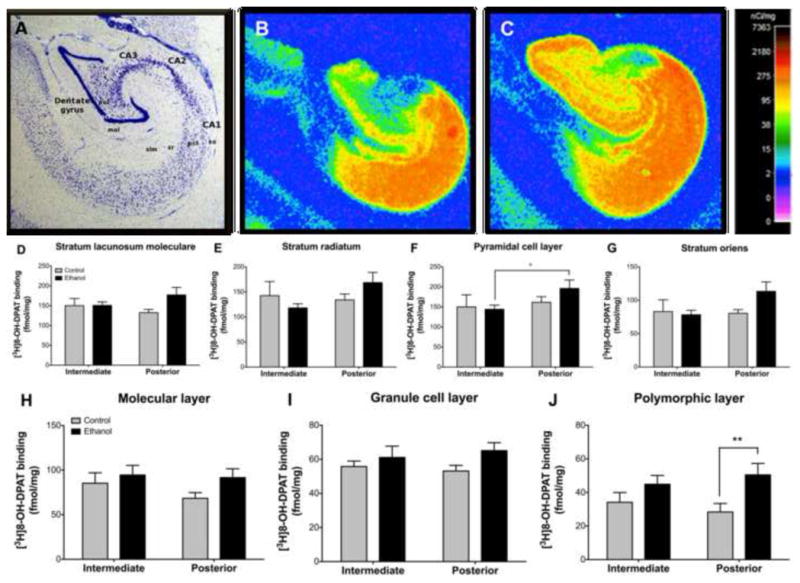
(A) Nissl stained section outlining the subregions and layers of the hippocampus. Representative control (B) and ethanol (C) autoradiograms showing high [3H]8-OH-DPAT binding in CA1 and moderate to high binding in the dentate gyrus. Binding was greater in ethanol drinkers in posterior CA1 than intermediate in the pyramidal cell layer (F) while controls exhibited similar binding between levels for both layers. No differences were observed in the stratum radiatum (E), stratum oriens (G) or stratum lacunosum moleculare (D). In the dentate gyrus, ethanol drinkers exhibited greater binding in the polymorphic layer (J) at the posterior level while no differences were observed in the molecular (H) or granule cell (I) layers. *p≤0.05; **p≤0.01. Abbreviations: CA1–3 – cornu ammonis 1–3; DG – dentate gyrus; gcl – granule cell layer; mol – molecular layer; pcl – pyramidal cell layer; pol – polymorphic layer; slm – stratum lacunosum moleculare; so – stratum oriens, sr – stratum radiatum.
