Figure 1.
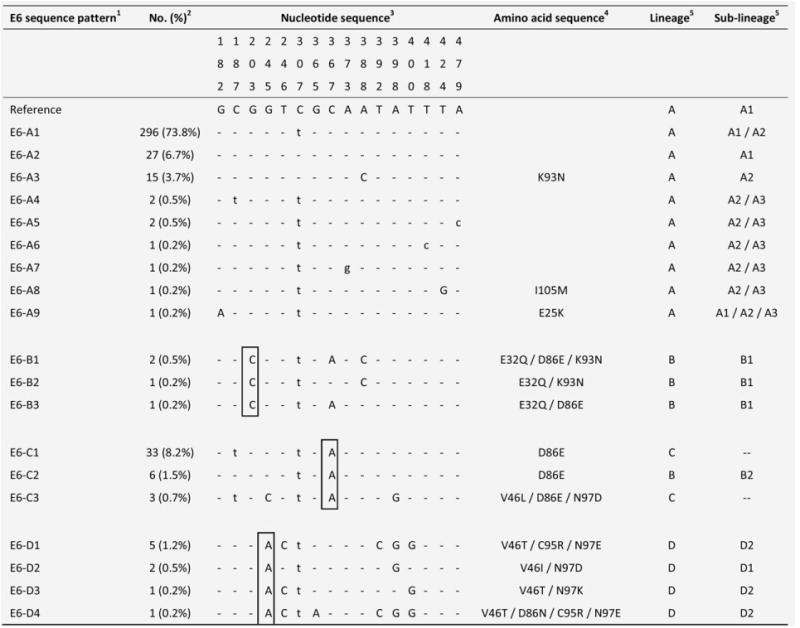
Nucleotide sequence variations at E6 of 19 HPV58 isolates.1 The group containing the prototype was assigned as E6-A. The HPV58 prototype (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/genbank accession no. NC_001443) was used as reference.2No. (%) of each sequence pattern found among the 401 samples examined.3 Nucleotide positions where variations were detected are written vertically across the top. Sites with no changes are marked with dashes. Capital letters indicate alternations result in an amino acid change. Lower case letters indicate synonymous mutations.4 The one letter amino acid code is used. The position of amino acid change is stated numerically. The letter preceding this number refers to the reference amino acid, and the letter following refers to its substitution.5 Lineage and sublineage classification based on full genome or concatenated E6-E7-E2-E5-L1-PCR sequences described in previous studies.15,16 Some E6 sequence patterns are not sublineage-specific. –, no sublineage assigned. Single nucleotide substitutions diagnostic for E6 variants are boxed. GenBank accession numbers for E6 sequences are KC190273 - KC190291.
