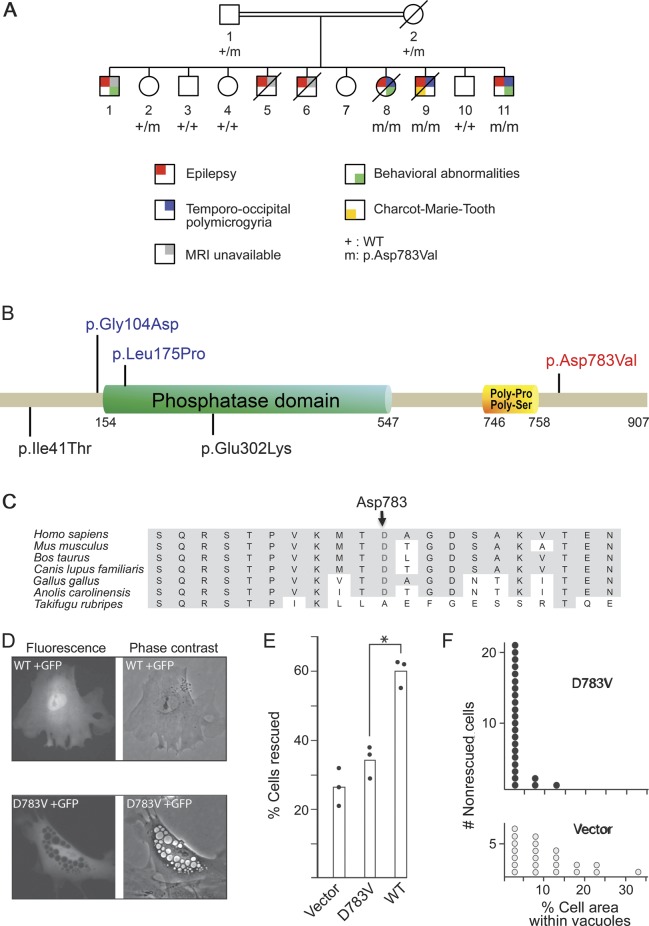
Figure 2. Identification of FIG4 mutation.
(A) Pedigree of the family with segregation of the FIG4 variant. Only generations IV and V are shown.13 (B) FIG4 is a multidomain protein with a protein interaction domain at the N-terminus, a SAC phosphatase domain in the central region, and poly-Pro and poly-Ser domains within the C-terminal. The mutation identified in this study is indicated in red, and missense mutations previously reported in Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type 4J21 and Yunis-Varón syndrome15 are indicated in black and blue, respectively. (C) Multiple protein alignment showing conservation of the aspartate (D) residue in position 783 in orthologs of FIG4 across species. (D) Phenotype rescue in Fig4-null fibroblasts of plt mice. Mutant or wild-type (WT) Fig4 cDNA was cotransfected with GFP into Fig4-null fibroblasts. The large intracytoplasmic vesicles characteristic of Fig4-null fibroblasts were rescued in 60% of cells by the WT cDNA (top panels) but in only 33% of cells by the D783V mutant cDNA (bottom panels). (E) Percent of transfected (GFP-positive) fibroblasts that lack vacuoles. The results of 3 independent experiments are indicated. *p < 0.01. (F) The D783V mutant retains partial activity. In nonrescued cells from panel E, the percentage of cell area covered by vacuoles in cells expressing D783V (3.3% ± 0.6%, n = 24) is smaller than that in cells receiving vector only (10.3% ± 1.8%, n = 22) (2-tailed p value <0.001). Transfection of the mutant cDNA does not completely rescue the formation of vacuoles but does reduce the severity of vacuolization. cDNA = complementary DNA; GFP = green fluorescent protein; plt = pale tremor.