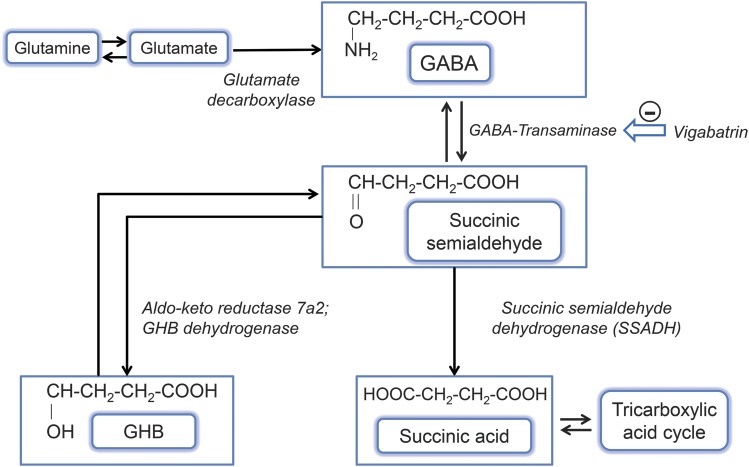
Figure. GABA catabolism pathway.
GABA (γ-aminobutyric acid) is normally converted via GABA-transaminase to succinate semialdehyde, which is then broken down to succinic acid by succinate semialdehyde dehydrogenase (SSADH). In the absence of SSADH, succinate semialdehyde is converted to γ-hydroxybutyric acid (GHB) rather than succinic acid, and this leads to a buildup of both GHB and GABA in the brain. Vigabatrin is an irreversible inhibitor of GABA-transaminase as shown.