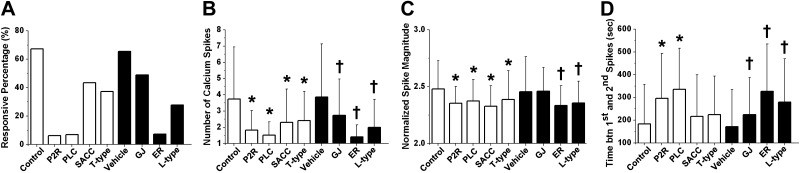
Figure 5.
Investigation of the roles of various Ca2+ signaling pathways in 6-N mechanical loading-induced Ca2+ oscillations. Extracellular ATP P2X/P2Y receptors (P2R), PLC, SACCs, T-type VGCCs (T-type), L-type VGCCs (L-type), GJs, and ER Ca2+ store (ER) have all been implicated in osteocyte Ca2+ signaling. These pathways were inhibited using small molecule inhibitors. A DMSO vehicle control was used for statistical comparisons of GJ, ER, and L-type groups. Percentage of responsive cells (A), average number of Ca2+ spikes (excluding nonresponsive cells; B), normalized spike magnitude (C), and time between first and second spikes (D) over the 15-min experimental period. *P < 0.05 vs. corresponding control group; †P < 0.05 vs. vehicle control group.