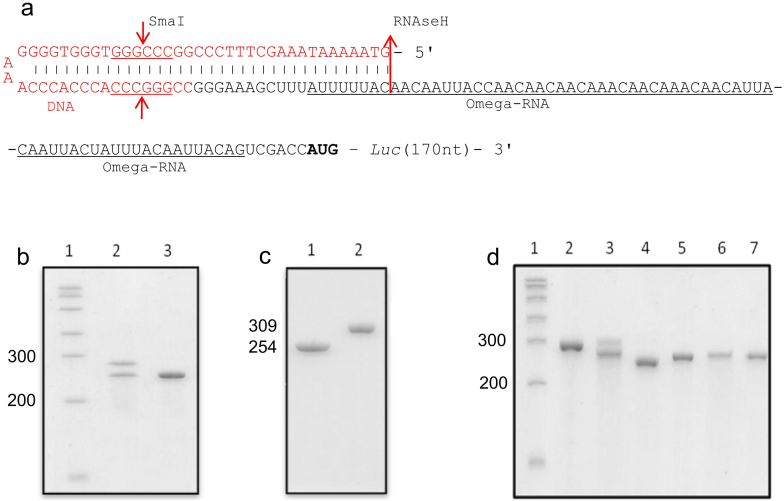
Figure 1. Blocking of the omega leader RNA and its experimental verification.
(a) Scheme of 5′-terminal blockade of the omega leader RNA with the synthetic oligodeoxyribonucleotide (see the text), which forms a stable untranslatable hairpin involving the 5′-end of the RNA. Black letters: the polyribonucleotide (RNA) comprising 67 nt long omega leader sequence (underlined); red letters: the blocking 55 nt long oligodeoxyribonucleotide containing SmaI restriction site (underlined). The arrows indicate the targets for restriction endonuclease SmaI and RNase H. The right-hand arrow at the end of the UTR sequence shows the start of the170 nt long RNA fragment encoding for the N-terminal part of firefly luciferase. The non-blocked mRNA construct consists of 254 nt and the ligation procedure yields a mixed polydeoxyribo-polyribonucleotide product of 309 nt in length. (b, c, d) Electrophoretic analyses of the polynucleotide preparations in denaturing 6% PAGE. (b) Analysis of the ligation reaction products: 1, standard RNA markers (100–1,000 nt); 2, the result of the ligation reaction of the RNA with the blocking oligodeoxyribonucleotide (the upper band corresponds to the blocked RNA); 3, the initial unblocked RNA. (c) Analysis of the blocked RNA after purification in PAGE: 1, unblocked RNA; 2, purified blocked RNA ligated with oligodeoxyribonucleotide. (d) Analysis of specificity of the ligation reaction product: 1, RNA markers (the same as in B); 2, the RNA blocked with the oligodeoxyribonucleotide; 3, the blocked RNA after treatment with endonuclease SmaI; 4, the blocked RNA after treatment with RNase H; 5, the unblocked RNA; 6, the unbloched RNA after treatment with endonuclease SmaI; 7, the unblocked RNA after treatment with RNase H.