Figure 5.
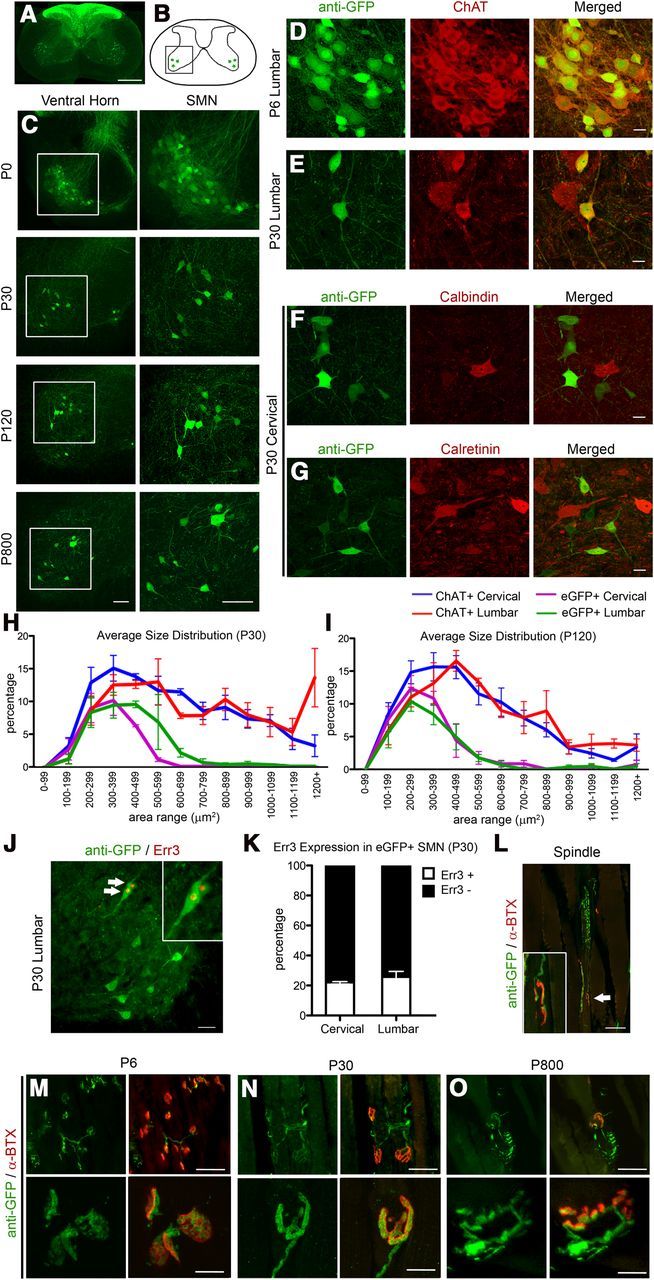
eGFP+ neurons in the spinal cord of UCHL1-eGFP mouse display cellular and molecular characteristics of SMN. A, Axial spinal cord section showing eGFP+ DRG afferents in the dorsal horns and eGFP+ cells in the ventral horns. B, Drawing of spinal cord. Boxed area represents the ventral horn. C, Images of ventral horn at P0, P30, P120, and P800. Boxed areas enlarged to the right. D, E, eGFP+ neurons express ChAT at P6 (D) and at P30 (E). F, G, eGFP+ do not express interneuron markers, such as calbindin (F) and calretinin (G). H, I, Average size distribution of eGFP+ and ChAT+ SMN in cervical and lumbar spinal cord of UCHL1-eGFP mice at P30 (H) and at P120 (I). J, Subset of eGFP+ neurons expresses γ motor neuron marker Err3 (arrows, enlarged in inset). K, Bar graph representation of percentage Err3 expression in eGFP+ SMN at P30. L, Image of a representative eGFP+ γ motor neuron axon (arrow, enlarged in inset) innervating the intrafusal muscle fiber NMJ identified by postsynaptic marker α-bungarotoxin (α-BTX). M–O, Low-magnification (top) and high-magnification (bottom) images of gastrocnemius muscle showing eGFP+ axons innervating extrafusal NMJ at P6 (M), P30 (N), and P800 (O). Scale bars: A, 500 μm; C, 100 μm; D–G, 20 μm; J, L, 50 μm; M–O, 50 μm (top) and 10 μm (bottom).
