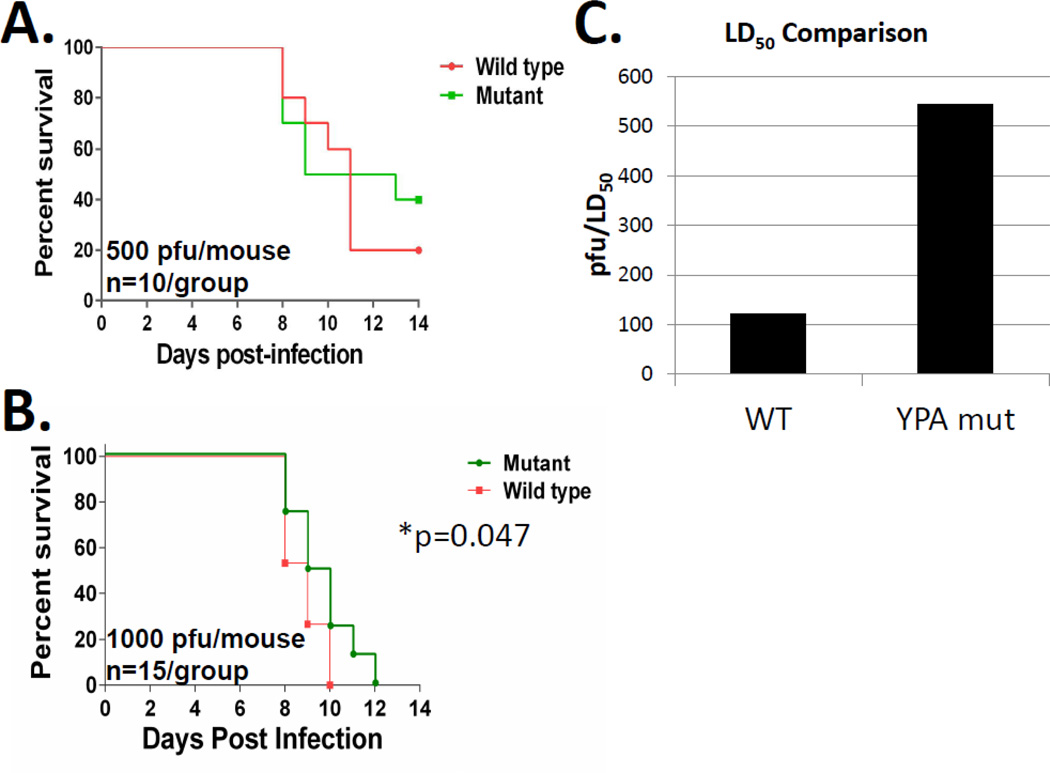
Figure 9. Mutation of the YPD motif results in virus attenuation in a BALB/c mouse model of infection.
Female BALB/c mice were intranasally inoculated with 500 (panel A, total n=10, 2×group) or 1000 PFUs (panel B, total n=15, 1×5/group and 1×10/group) of either mutant (Mut) or wild type (WT) virus. Mice were followed for 14 (panel A) or 12 (panel B) days after infection and death was defined as a greater than 20% (panel A) or 30% (panel B) reduction in initial body weight and used to generate survival curves. The asterisk in panel B represents a statistically significant difference (Log-rank, Mantel Cox test) in time to death between the WT and mutant infected groups. Panel C. Mouse lethal dose 50% (LD50’s). Mice were inoculated with different doses of either the wild type or the mutant viruses and followed for survival for 14 days. Mice that lost more than 25% of their initial body weight were considered dead and humanely euthanized accordingly. LD50s were calculated using the method of Reed and Muench59. The bar graphs represent the LD50 values for both the WT and mutant viruses.