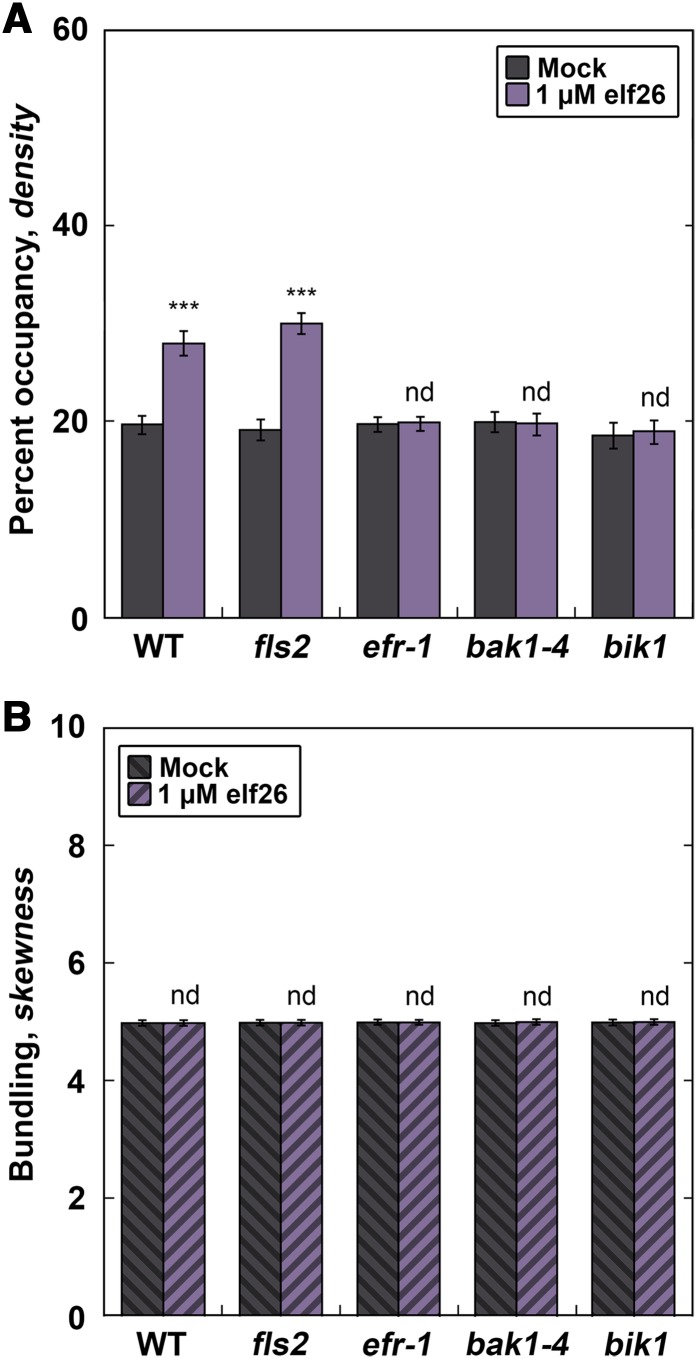
Figure 2.
Recognition of elf26 by the EFR Receptor Complex Is Required for the Increase in Actin Abundance.
(A) Arabidopsis knockout mutants define the early signaling steps required for increased actin abundance in hypocotyl epidermal cells. Filament abundance was measured in epidermal cells from homozygous signaling mutant seedlings expressing GFP-fABD2 following 5 min of treatment with 1 µM elf26 or mock. Columbia-0 expressing GFP-fABD2 was used as the wild-type control. Knockout lines for EFR and components of the PRR complex, BAK1 and BIK1, were used to define the host-signaling components required for eliciting the actin response. Wild-type and fls2 homozygous mutant seedlings exhibit enhanced filament abundance following 1 µM elf26 treatment, whereas knockout mutants for the EFR-PRR complex (i.e., efr-1, bak1-4, and bik1) did not have a measurable change compared with the mock control.
(B) The extent of actin filament bundling was not significantly different from mock-treated controls. Images used for analysis in (A) were measured for filament bundling.
Values given are means ±se (n = 300 cells per genotype from at least 30 hypocotyls). Asterisks represent significant differences by ANOVA, with Tukey HSD posthoc analysis (nd = not significantly different from mock; ***P < 0.001).