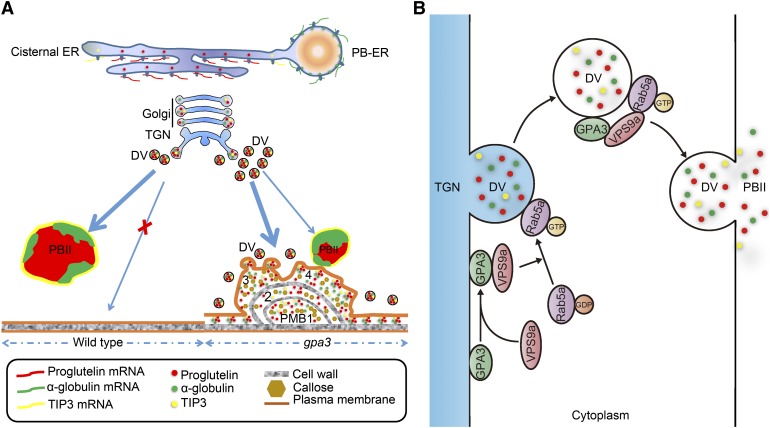
Figure 8.
Working Model Depicting the Function of GPA3 in Vacuolar Protein Sorting in Rice Endosperm.
In the wild type, proglutelins and α-globulins are separately synthesized in the cisternal ER and protein body ER, and both of them converge in the Golgi apparatus, where they are packaged together into DVs, and then directly targeted to the PSV (PBII). The PSV marker protein TIP3 follows the same route to the PSV (PBII) with proglutelins. In the gpa3 mutant, directional targeting of DVs to the PSV (PBII) is severely blocked. Therefore, numerous DVs are mistargeted to the PM, and via membrane fusion, releasing their contents into the apoplast to form PMBs, in which massive amounts of cargo proteins, including proglutelins, α-globulins, and TIP3, as well as cell wall components abnormally accumulate (A). It can be speculated that GPA3 most likely functions as an adaptor protein to recruit VPS9a (Rab5a-GEF) and facilitate the interaction between Rab5a and VPS9a on the TGN and DVs, which is required for proper membrane fusion and/or directional targeting of DVs to the PSV (PBII [B]).