Figure 1.
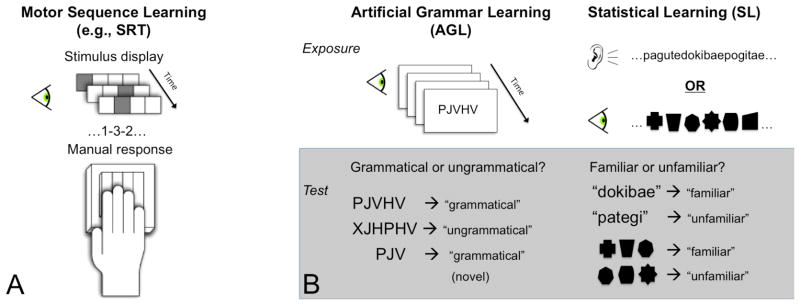
Structure of various learning paradigms relevant to this review. (A) Motor Sequence Learning: Participants initiate a motor response to temporally-patterned visual stimuli. (B) Artificial Grammar Learning and Statistical Learning: Participants undergo an exposure phase during which they are presented with finite-state grammar sequences (AGL) or probabilistic auditory/visual patterns (SL). In a subsequent test phase, they make acceptability judgments on structured and unstructured test items.
