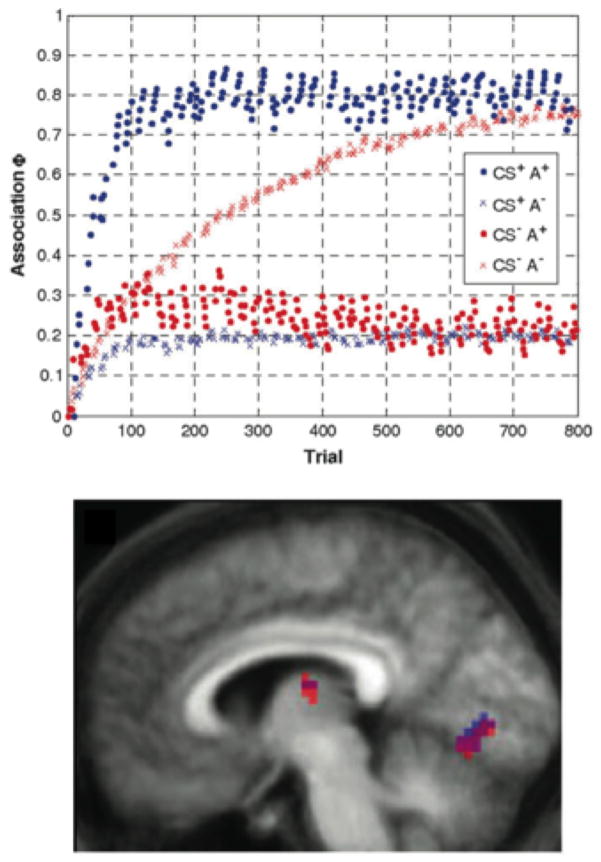
Figure 5.
Classic computational model (Rescorla-Wagner model) examining the effects of incidental, associative learning on cortical connectivity (from den Ouden et al. A dual-role for prediction error in associative learning. Cerebral Cortex, 2009, 19, pp. 178, 180, by permission of Oxford University Press). Top panel: parameter estimates of associative strength from the model for each stimulus condition in a 2x2 design (presence or absences of the conditioned visual stimulus, CS+ vs CS-, and presence or absence of the predictive auditory stimulus, A+ vs. A-). Bottom panel: a subset of the regions of interest that showed modulation of activity by experimental condition but also model-estimated associative strength.