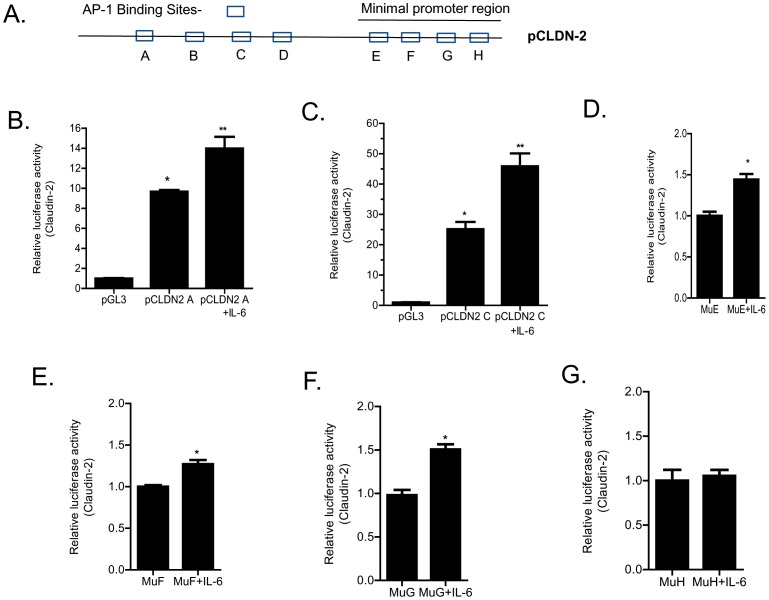
Figure 10. Identification of DNA binding sequence responsible for IL-6 induced increase in claudin-2 promoter activity.
(A) Schematic diagram showing 8 potential AP-1 binding sites within the claudin-2 promoter region. Four binding sites were located outside the minimal promoter region (trans-AP-1) and four sites were within the minimal promoter region (cis-AP-1). (B) IL-6 treatment caused an increase in promoter activity in the FL promoter construct (pCLDN2 A) (n = 6). *, p<0.001 vs. control; **, p<001 vs. IL-6 treatment. (C) IL-6 caused a similar increase in promoter activity in the deletion construct lacking the trans-AP-1 sites (pCLDN2 C) (n = 6). *, p<0.001 vs. control; **, p<001 vs. IL-6 treatment. The site-directed mutagenesis of three up-stream cis-AP-1 binding sequences (E, F, G) did not affect the IL-6 induced increase in claudin-2 promoter activity (D), (E), (F) (n = 6). *, p<0.001 vs. control; **, p<001 vs. IL-6 treatment. The mutation of the down-stream cis-AP-1 binding (sequence H) prevented the IL-6 induced increase in claudin-2 promoter activity (n = 6) (G).