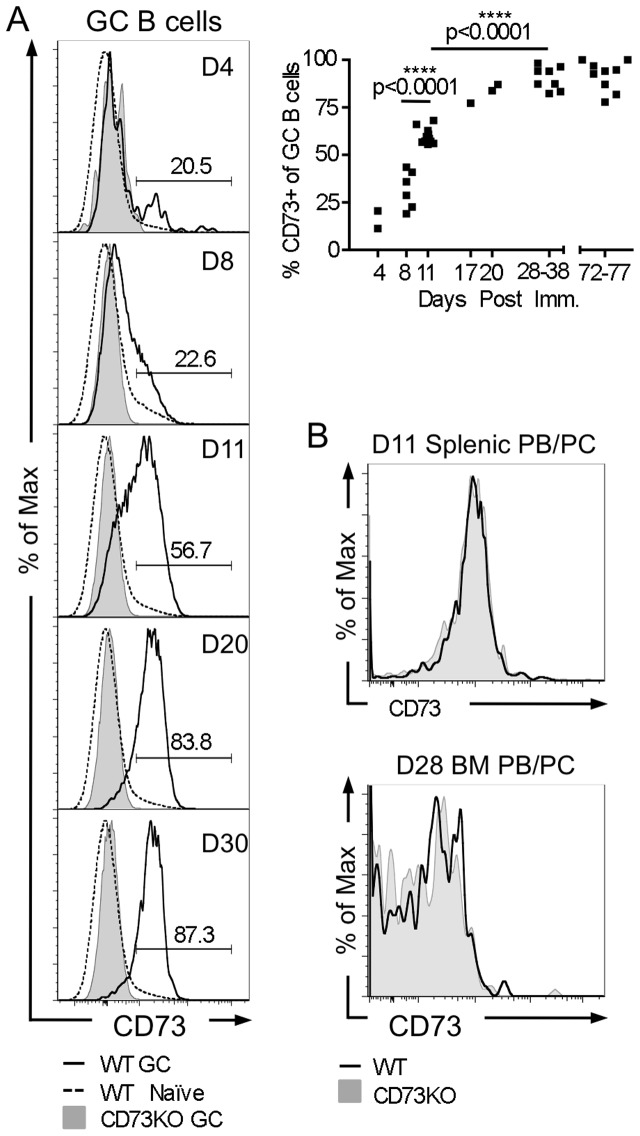
Figure 1. CD73 expression is modulated among responding antigen-specific B lineage cells in response to immunization with T-dependent antigen.
Splenocytes and BM cells from B6 WT and control CD73KO mice were stained and analyzed by flow cytometry on the indicated days post i.p. immunization with NP-CGG in alum. Representative FACS histograms of CD73 expression are shown. 3 million events were collected per sample. (A) CD73 expression on splenic GC B cells from WT (solid line) or CD73 KO (shaded gray), identified as NIP+ kappalo CD38low CD95hi CD19+. For comparison, staining of WT kappa+ CD38hi CD95lo CD19+ cells, which are predominately naïve, is shown (dashed line). (Upper right) Percentage of CD73+ GC B cells as a function of time; each point represents an individual mouse. On days 72–77, GC B cells were gated as NIP+ kappalo CD95hi CD19+ (without CD38 gating). (B) CD73 staining of PB/PC populations from the spleen and marrow of WT (solid line) and CD73KO (shaded gray) mice. Antigen specific splenic and BM PB/PC populations were identified as intracellular NIP5BSAhi surface B220−, and were a mixture of CD138hi and CD138lo cells. Similar results were seen when gated on IgG1 hi.