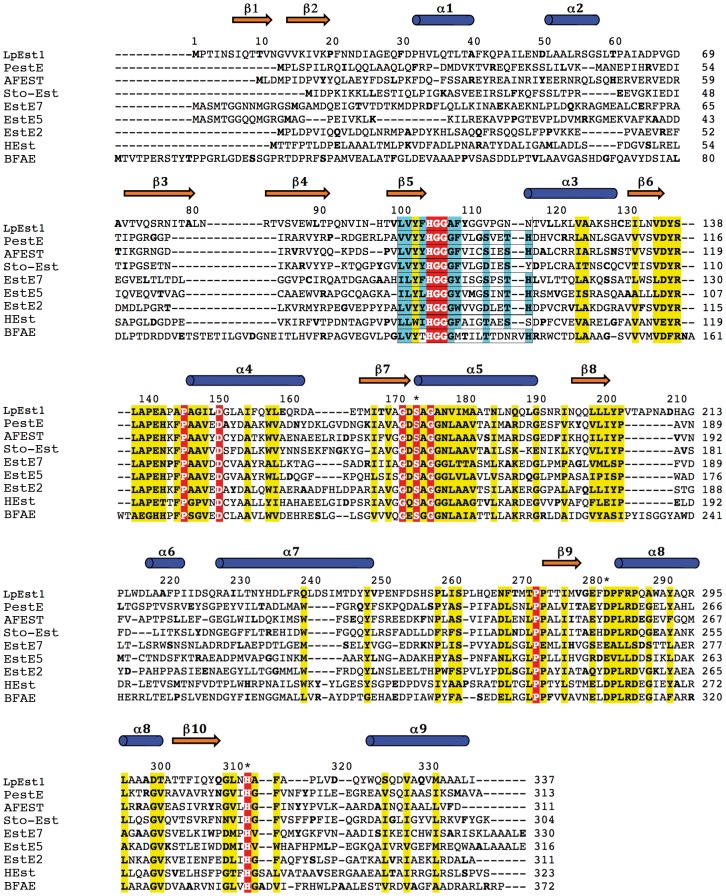
Figure 1. Protein sequence alignment between LpEst1 and homologs from the hormone-sensitive lipase (HSL) family.
PestE, carboxylesterase PestE from Pyrobaculum calidifontis; AFEST, carboxylesterase AFEST from Archaeoglobus fulgidus; Sto-Est, thermophilic esterase Sto-Est from Sulfolobus tokodaii; EstE7, esterase EstE7 from environmental samples; EstE5, esterase EstE5 from environmental samples; EstE2, thermophilic esterases EstE2 from Alicyclobacillus acidocaldarius; HEst, heroin esterase from Rhodococcus sp.; BFAE, Brefeldin A esterase from Bacillus subtilis. Residues from LpEst1 in Residues from LpEst1 in sterase fblue cylinders and orange arrows, respectively. Residues forming the catalytic triad are marked with an asterisk. Colour code for boxes is as follows: red, conserved residues in all proteins; yellow, highly conserved positions; cyan, residues that coincide with the expected canonical sequence motif characteristic of enzymes from the HSL family.