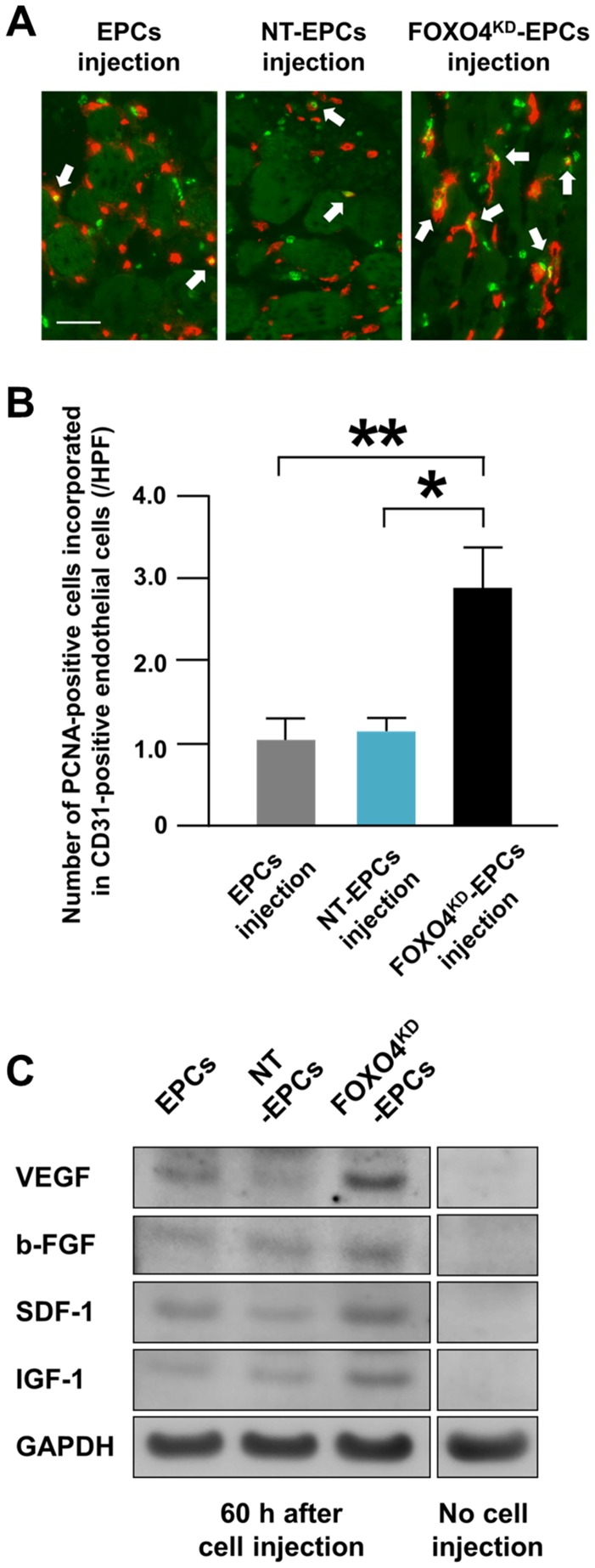
Figure 10. Kinetics of EPCs for neovascularization in vivo.
(A) Representative fluorescence microscopic images of EPCs incorporated in endothelial cells of the ischemic limbs of athymic nude rats 60 h after intramuscular injection of EPCs, NT-EPCs, or FOXO4KD-EPCs. Rat specific CD31-positive endothelial cells were stained red. Human specific PCNA-positive cells, which were defined as human-derived EPCs, were stained green. Scale bar: 50 μm. (B) Pooled data of the number of PCNA-positive EPCs incorporated in endothelial cells of the rat ischemic limbs 60 h after the injection of EPCs, NT-EPCs, or FOXO4KD-EPCs (*: p<0.01; **: p<0.005; n = 5, each). (C) A representative western blotting photo of expressions of human specific VEGF, b-FGF, SDF-1, and IGF-1 in the rat ischemic limb 60 h after intramuscular injection of EPCs, NT-EPCs, or FOXO4KD-EPCs (n = 4, each).