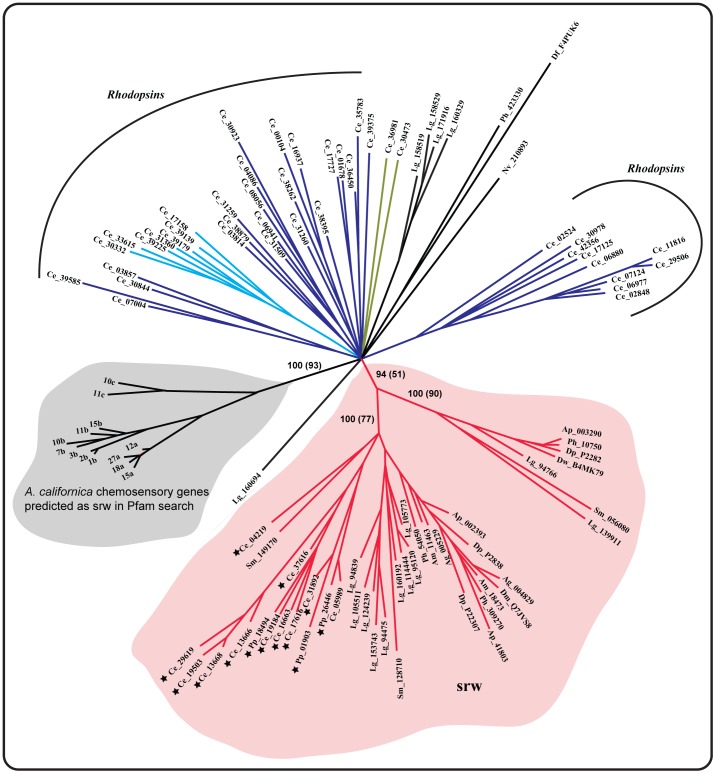
Figure 2. Phylogenetic relationships of the Rhodopsin subfamilies, the srw family from C. elegans and the srw like sequences identified from several protostome species.
The tree topology was inferred from Bayesian analysis with a gamma correction using MrBayes software. The Rhodopsin subfamilies from C. elegans included the peptide (violet), amine (light blue) and the SOG (olive green) subfamilies, among others. The major clade that clustered the novel srw like sequences with the known srw family members from nematodes (C. elegans and P. pacificus) is highlighted in red (the conserved 7TM regions of the sequences from srw clade are shown in Figure S2). Previously known srw family members from nematodes (C. elegans and P. pacificus) are marked with a star symbol. Sequences that had the highest alignment score against the 7tm_GPCR_srw domain, but failed to cluster within the srw clade are marked with black edges. Similarly, the chemosensory genes in A. californica that had the highest alignment score against the 7tm_GPCR_srw domain in our Pfam search, but clustered separately from the srw family members from nematode is highlighted in grey. We followed the same renaming for the A. californica genes as previously used [36] for easy cross verification. Abbreviations used in the figure includes, Ap (Acyrthosiphon pisum), Ag (Anopheles gambiae), Am (Apis mellifera), Ce (Caenorhabditis elegans), Df (Dictyostelium fasciculatum), Dm (Drosophila melanogaster), Dp (Daphnia pulex), Dw (Drosophila willistoni), Lg (Lottia gigantea), Ph (Pediculus humanus), Pp (Pristionchus pacificus), Sm (Schistosoma mansoni) and Nv (Nematostella vectensis). Posterior probabilities and bootstrap replicates (within parenthesis) are shown as a percentage for the major nodes.