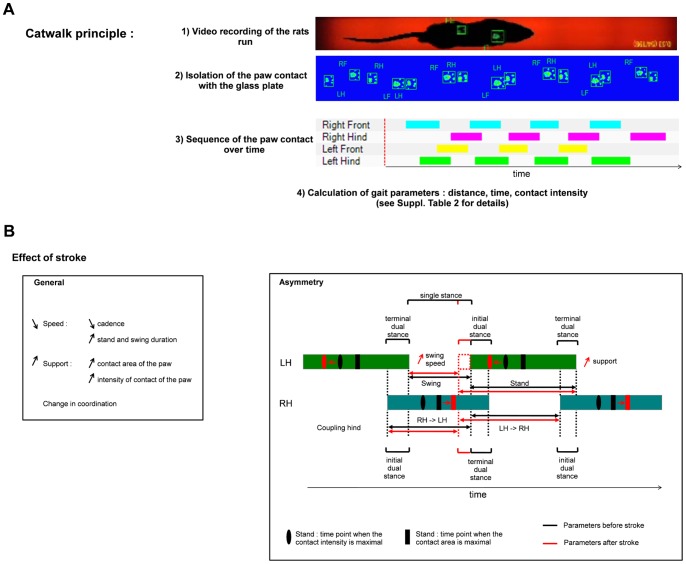
Figure 4. Effect of stroke on gait.
Presentation of gait parameters and the changes induced by PT. (A) Principle of the Catwalk. Rats run on a glass plate illuminated from the side. When the paws press the plate, light is diffracted and captured by a camera below the glass plate. The calculation of the gait parameters require the following steps: 1) the runs are recorded, 2) the light spots are associated with their respective paws, 3) the sequence of paw contact with the glass plate over time is determined and 4) the different gait parameters are calculated. (B) Stroke induces changes in different gait parameters. Here are summarized the general effect of stroke on gait two days after stroke. (C) Stroke also induces an asymmetry between left and right side in some gait parameters. The colored boxes represent time fractions when the paws are in contact with the surface of the glass plate. The black lines represent the values before stroke and the red lines the direction as well as increase or decrease of the values at 2 days after stroke (LH: left hind limb, RH: right hind limb). For details see Table S3.