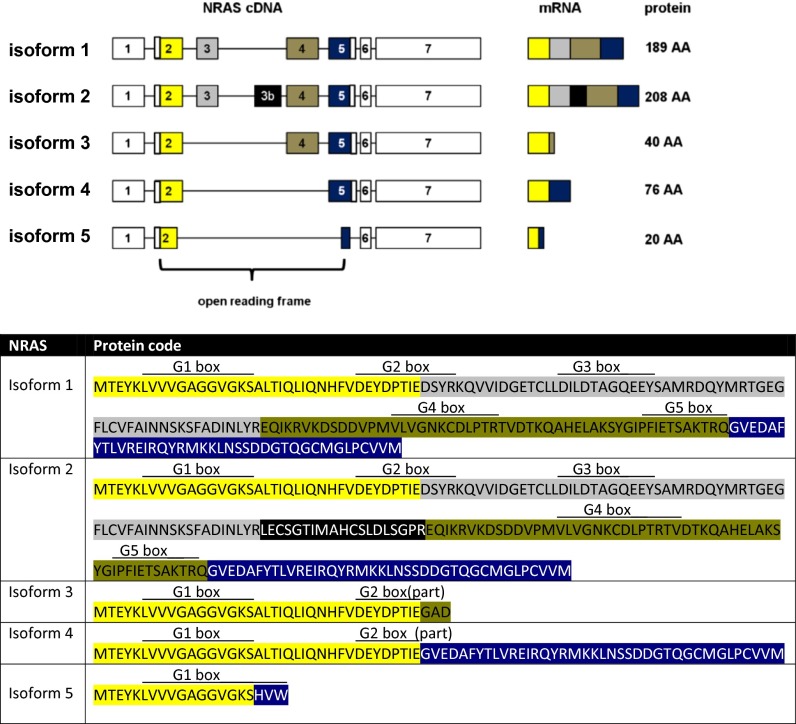
Fig. 1.
(Upper) Characterization of the five naturally occurring NRAS isoforms. Isoform 1 is the hitherto known NRAS isoform. Isoform 2 contains a previously unknown exon 3b. Isoforms 3 and 4 are lacking exon 3 or exons 3 and 4, respectively. Isoform 5 is the result of the fusion of the first 17 codons of exon 2 with 3 codons toward the end of exon 5. The graph displays cDNA, splicing products (mRNA), and corresponding protein lengths of the isoforms. Exons included in the ORF are colored. (Lower) Predicted protein codes of the five NRAS isoforms, with color codes highlighting the different exons (yellow, exon 2; gray, exon 3; black, exon 3b; khaki, exon 4; blue, exon 5). Locations of the G boxes are indicated above the predicted codes [simplified presentation, locations, and functional descriptions adapted from Colicelli (26)]: G1 box, P-loop, purine nucleotide binding; G2 box, GDP/GTP binding and effector binding; G3 box, Mg2+ ion binding; G4 box, hydrogen bond contact with the guanine ring, interaction with G1 box; G5 box, guanine nucleotide association.