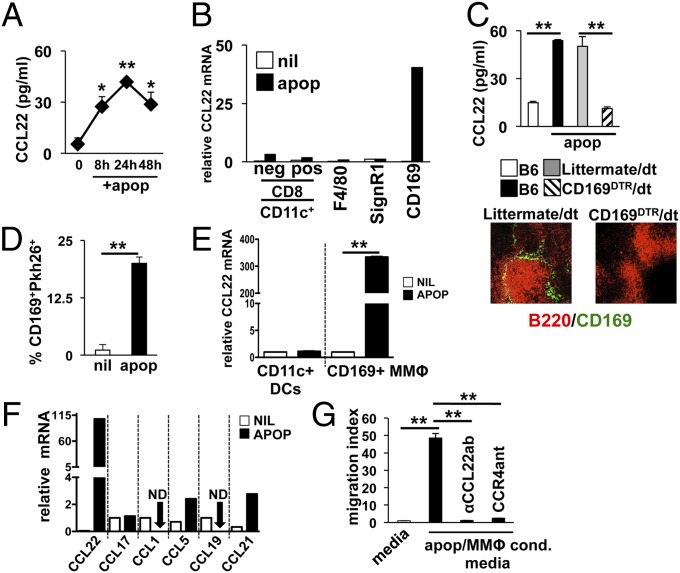
Fig. 1.
Apoptotic cells induce CCL22 expression in splenic CD169+ metallophillic macrophages. (A) B6 mice were injected with 107 apoptotic thymocytes i.v. and at indicated time points, whole-spleen lysates were tested for CCL22. (B) At 4 h after apoptotic cell injection as in A, phagocytes were sorted based on indicated markers by FACS, and CCL22 message was measured by sqPCR. (C) B6.CD169DTR mice were depleted of MMΦs as described (13) and injected with apoptotic thymocytes as described in A. At 24 h later, CCL22 protein was measured in whole-spleen lysates by ELISA. Immunofluorescence shows representative spleen sections from B6.CD169DTR and littermate control groups 48 h after last injection with diphtheria toxin stained for B-cell markers (αB220, red) and αCD169 (green). (D) Splenic CD169+ cells were analyzed by FACS for uptake of Pkh26-labeled apoptotic cells 30 min after injection with 107 cells i.v. (E) CD169+ and CD11c+ cells were sorted from B6 mice and cultured in complete RPMI with apoptotic thymocytes at a 10:1 apoptotic cell/phagocyte ratio for 4 h. CCL22 message was then measured by sqPCR as described. (F) At 4 h after apoptotic cell injection as in A, CD169+ MΦs were sorted by FACS and chemokine message for the species indicated was measured by sqPCR. (G) FACS-purified splenic CD169+ macrophages were incubated with apoptotic cells at a 10:1 ratio. At 24 h, supernatant from the cultures were analyzed for chemotactic activity against MACS-purified CD4+CD25+ Tregs. In some wells, neutralizing αCCL22 antibody or CCR4 antagonist was added to confirm the dependence of migration on CCL22-dependent mechanisms as described in Materials and Methods. Bars represent mean value for five mice ± SD (A, C, and D), pooled samples from three mice (B and F), or triplicate wells (E and G). *Pval ≤ 0.05; **Pval < 0.01 as determined by Student t test. Experiments were repeated at least three times with similar results. ND, not detected.