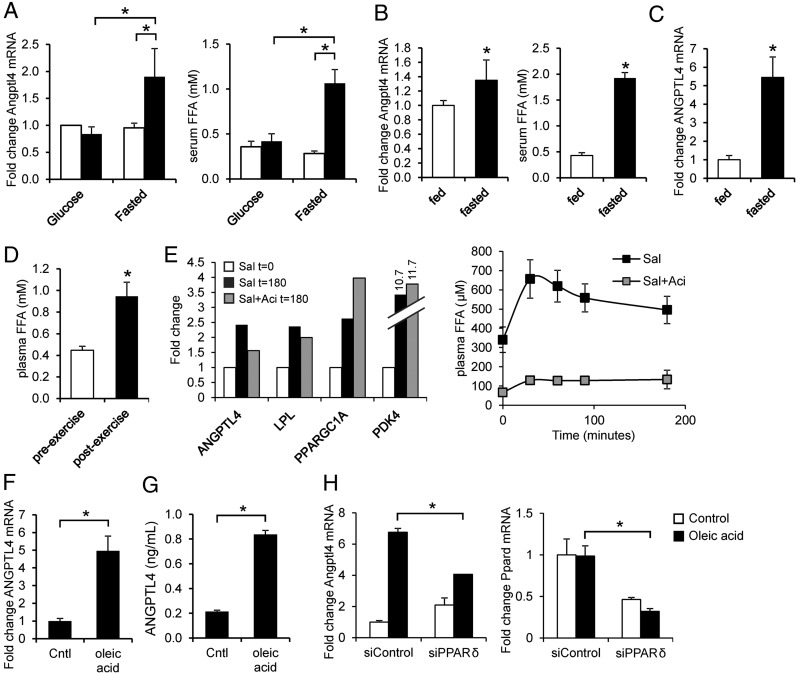
Fig. 4.
Sensitive induction of the ANGPTL4 gene by FFAs in human and mouse myocytes. (A) C2C12 myotubes were incubated for 6 h with 10% serum from subjects (n = 5) before exercise (white bar) and after exercise (black bar) performed in fasted state or with provision of glucose (study E). (Left) Angptl4 mRNA. (Right) Serum FFA levels. (B) C2C12 myotubes were incubated for 3 h with 10% serum from subjects (n = 12) at the end of a 60-h fast or after 60 h in the normal fed condition (study F). (Left) Angptl4 mRNA levels. (Right) Serum FFA levels. (C) ANGPTL4 mRNA in muscle biopsies collected at the end of the 60-h fast or after 60 h in the normal fed condition (study F). (D) Plasma FFA levels before and after one-legged exercise (n = 12). (E) (Left) Pooled mRNA expression of selected genes in muscle biopsies collected before and after salbutamol infusion with and without prior acipimox administration (study G, n = 9). (Right) Plasma FFA levels during salbutamol (Sal) infusion. Error bars represent SEM. (F and G) ANGPTL4 mRNA (F) and ANGPTL4 (G) concentration in medium in primary human myotubes treated with oleic acid. (H) Angptl4 and Ppard mRNA in C2C12 myotubes transfected with control (nontargeting) or with PPARδ siRNA and treated with oleic acid. *Significantly different according to Student t test (P < 0.05). Error bars represent SD unless otherwise indicated. Cells were treated for 12 h unless otherwise indicated.