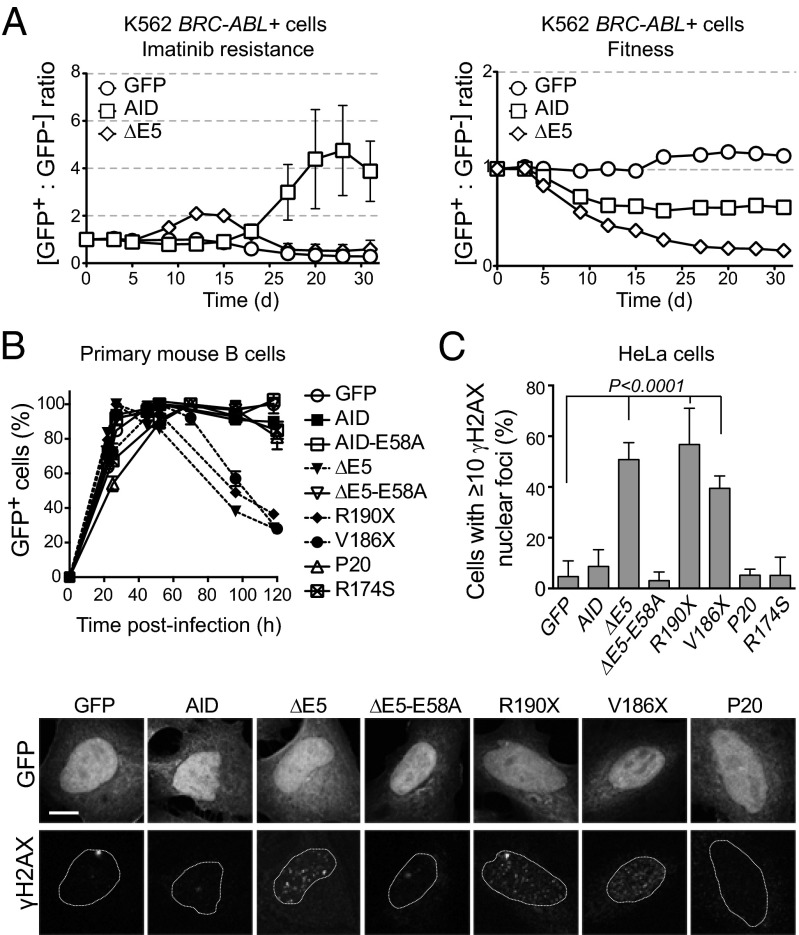
Fig. 3.
CSR-deficient dominant-negative AID variants are genotoxic. (A) Follow-up of the ratio of K562 BCR-ABL+ cells originally sensitive to imatinib transduced with AID-ires-GFP (GFP+) or untransduced (GFP−). Cells were grown in the presence of imatinib (Left), where the increase in the GFP+/GFP− cells ratio indicates acquisition of imatinib resistance, or without selection (Right), where decrease in the GFP+/GFP− cells ratio reflects the effect of each AID variant on cell fitness. One representative experiment out of three experiments performed is shown. (B) Effect of AID variants on the expansion of retrovirally complemented Aicda−/− splenic B cells evaluated from the relative proportion of GFP+ (complemented) cells in the culture at various times postinfection. Mean + SEM proportion of GFP+ cells in B-cell cultures from two independently infected mice. One of two similar experiments is shown. (C) DNA damage accumulation in HeLa cells transiently expressing AID- or variant-ires-GFP was measured by the presence of γH2AX nuclear foci 48 h posttransfection. Means + SDs proportions of GFP+ cells with ≥10 foci from three to five independent experiments are plotted for each variant with ANOVA and Dunnet posttest P values. Representative confocal images are shown below.