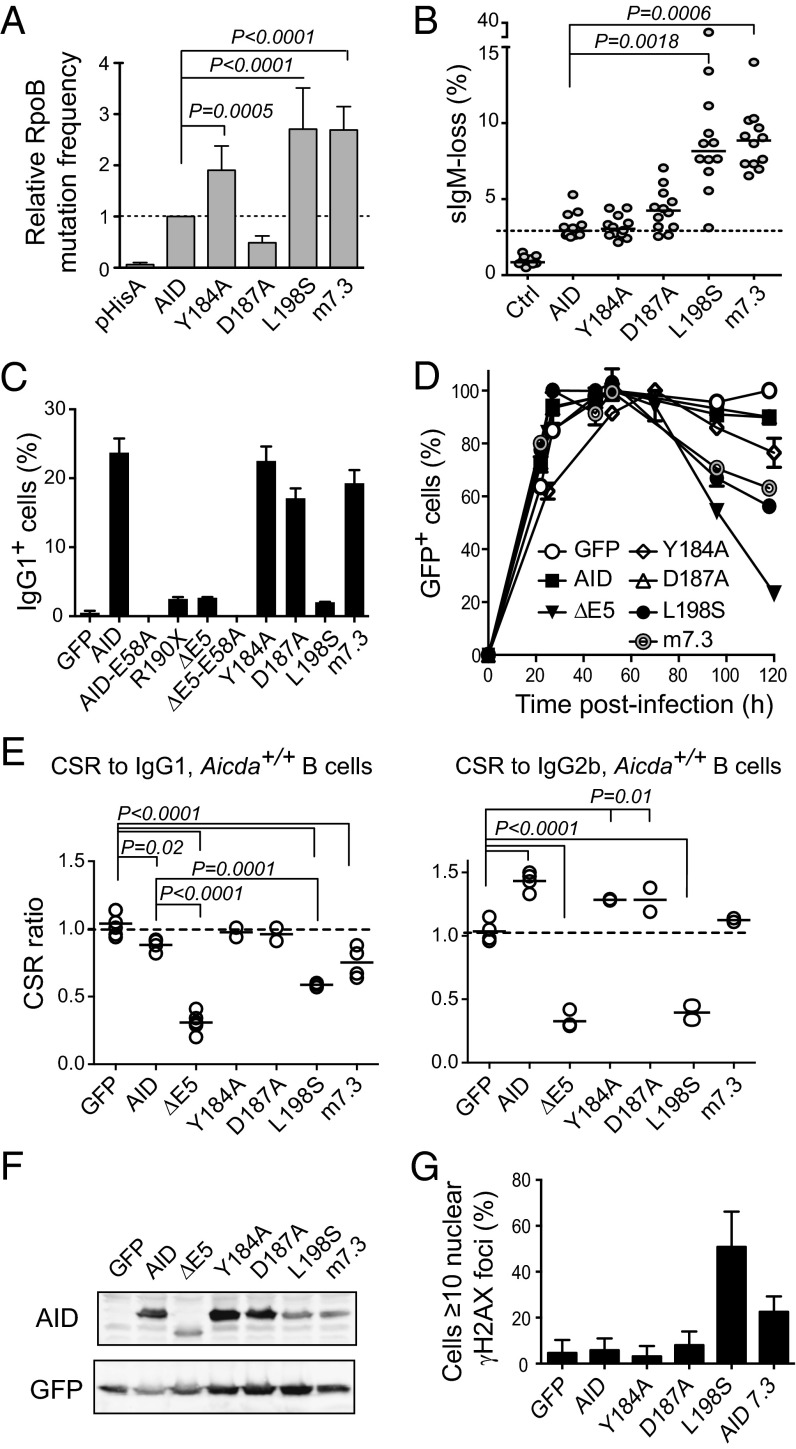
Fig. 4.
Dominant-negative ability of CSR-deficient AID variants correlates with DNA damage accumulation. (A) E. coli rpoB mutation frequency by AID single point mutants or variant m7.3 (bearing mutations K34E, T82,I and E156G). Means + SEMs of the relative medians normalized to AID from two to three independent experiments are plotted with significant P values from one-way ANOVA with the Holm–Sidak posttest. (B) SHM assay by IgM-loss fluctuation analysis in complemented DT40 ΔψVL Aicda−/− B cells. Each symbol is the percent of IgM− cells in an individual population after 2 wk of expansion; horizontal lines are median values for each population, with significant P values by Kruskal–Wallis test with Dunnet posttest comparison indicated. One representative experiment of two experiments is shown. (C) IgG1 CSR activity of AID variants in complemented mouse Aicda−/− B cells 4 d after stimulation with LPS + IL-4. Mean + SEM of two mice for each variant. (D) Effect of AID variants expression on the expansion of Aicda−/− splenic B cells transduced with AID variants-ires-GFP vectors. Mean ± SEM proportion of GFP+ cells over time postinfection in B-cell cultures from two mice. One representative experiment of two experiments is shown. (E) CSR dominant-negative assays for the indicated mutants like in Fig. 1. Each symbol is the CSR ratio of B cells transduced with AID- or variant-ires-GFP to uninfected cells from an individual mouse. Means (lines) and significant P values from one-way ANOVA with Dunnet posttest are indicated. (F) Protein expression level of AID variants by Western blot in packaging cells. (G) DNA damage accumulation in HeLa cells transiently transfected with AID variants assessed by the presence of γH2AX foci at 48 h posttransfection. Mean + SEM proportion of transfected cells showing ≥10 γH2AX nuclear foci from two to three experiments for each variant is plotted.