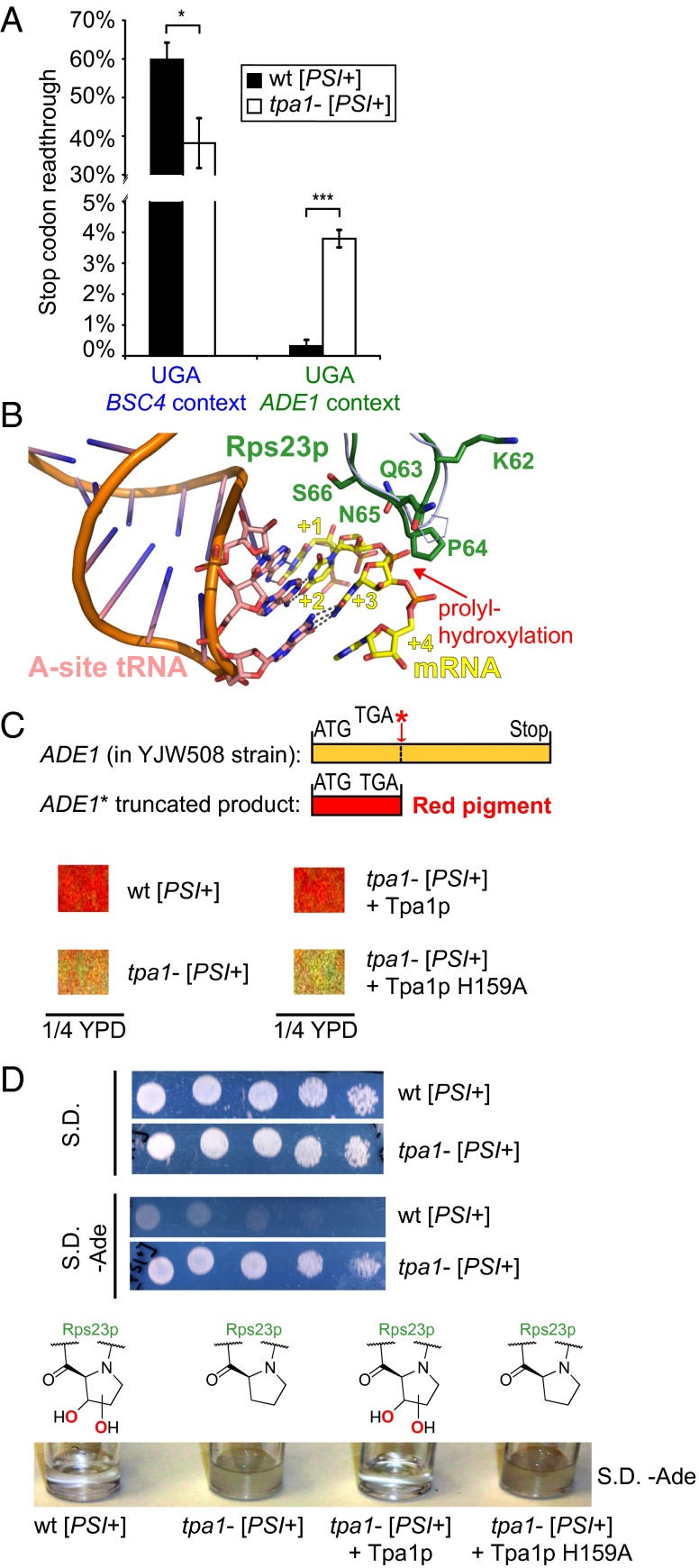
Fig. 3.
Physiological relevance of altered stop codon readthrough via Rps23p hydroxylation. (A) TPA1 deletion affects readthrough of the BSC4 and ADE1 stop codons (P = 0.012 and 0.00013, respectively) (n = 3; mean ± SD; *P < 0.05; ***P < 0.001; y axis interrupted for clarity). (B) View of the decoding site of the bacterial ribosome (17) with Rps23p (30) (green) modeled onto prokaryotic S12 (light-blue ribbon) (PDB ID codes 2J00, 2J01, and 3U5C). Integers indicate mRNA (yellow) codon positions. (C) TPA1 deletion leads to loss of red pigmentation as a consequence of increased readthrough of an ADE1 nonsense codon present in the YJW508 strain; this effect is reversed by plasmid rescue with WT Tpa1p but not an inactive variant (H159A). Views from suspension cultures in diluted yeast extract peptone dextrose (YPD) medium (Fig. S8E). (D) tpa1− but not WT YJW508 strains grow in medium lacking adenine both on agar (Upper; fivefold serial dilutions) and in suspension (Lower); an effect that is reversed by plasmid rescue with WT but not inactive (H159A) Tpa1p.