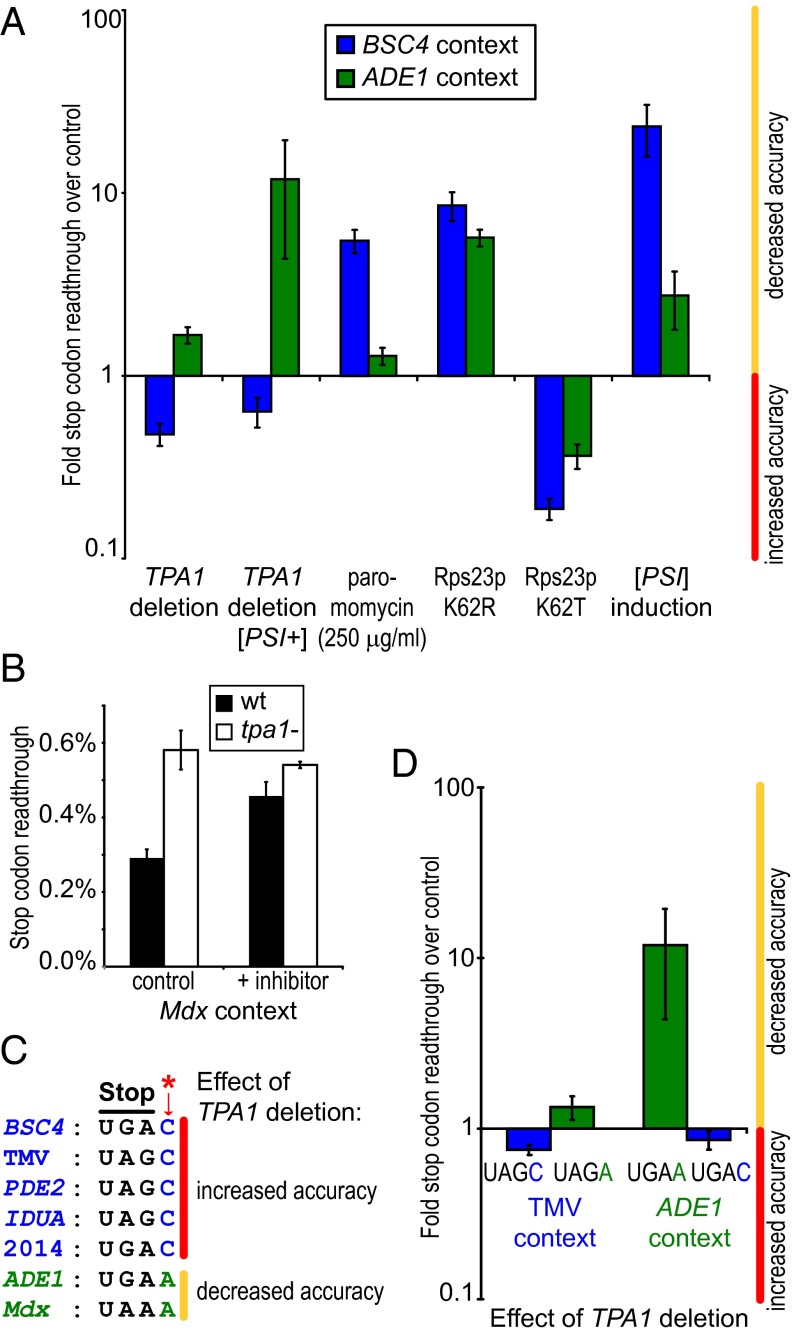
Fig. 4.
Effect of Rps23p hydroxylation on translation termination is sensitive to mRNA sequence context. (A) Whereas the directional effect of known accuracy modulators is sequence independent, TPA1 deletion reduces BSC4 but increases ADE1 readthrough (n = 3; mean ± SD; logarithmic y axis). Relative ratios refer to controls [WT BY4742, except for TPA1 deletion [PSI+] (WT [PSI+] YJW508) and PSI induction (WT [psi−] YJW508)]. (B) The generic 2OG oxygenase inhibitor dimethyloxalylglycine (10 mM) increases readthrough of the Mdx stop codon in WT but not tpa1− BY4742 strains (n = 2; mean ± SD). (C) Sequence alignment of tested stop codon contexts depicting the directional effect of Rps23p hydroxylation on readthrough (Fig. S2G). (D) Swapping of the +4 nucleotide within TMV and ADE1 termination sequences inverts the directional effect of TPA1 deletion on readthrough in BY4742 and YJW508 [PSI+] strains, respectively. Relative ratios refer to WT controls (n = 3; mean ± SD; logarithmic y axis).