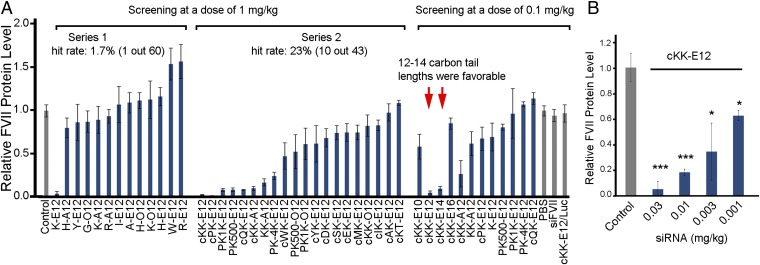
Fig. 3.
Identification of lead material cKK-E12 LPNs in mice. (A) LPNs were tested at a dose of 1 mg/kg in mice, which indicated that lysine was a favorable amino acid. Then, we investigated lysine-based peptide and polypeptide–lipid derivatives at the same dose. The hit rate was improved from 1.7% to 23% (including those compounds not screened due to particle instability or no entrapment of siRNA). The top hits and their analogs were explored at a lower dose of 0.1 mg/kg, which led to selection of cKK-E12 as the lead compound. Control, PBS; siFVII, FVII siRNA; cKK-E12/Luc, luciferase siRNA-formulated cKK-E12 LPNs. (B) Dose-dependent silencing of cKK-E12 in mice. K-E12, K, lysine; E, epoxide; A, aldehyde; O, acrylate; 12, carbon tail length. cKK-E12, c, cyclic. Data points represent group mean ± SD (n = 3 or 4; *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.005; t test, double-tailed).