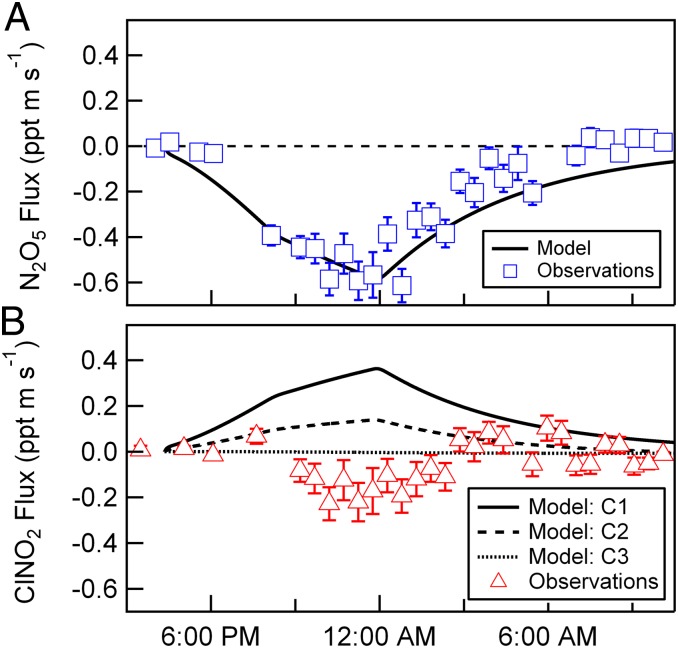
Fig. 2.
Measured vertical fluxes of N2O5 and ClNO2. Errors are determined for each 30-min flux segment as the covariance between vertical wind speed and concentration at lag times significantly longer than the delay (or lag) time. Calculated ClNO2 vertical fluxes (lines in B), as determined from the coupled time-dependent ocean−atmosphere model, constrained by the measured N2O5 vertical fluxes (A). Three different model scenarios are shown and described in detail in SI Text: C1 (a priori), model inputs taken as suggested in the literature [e.g., KH (ClNO2) = 1.66, Φ (ClNO2)ocean = 0.8, kr = 5 × 106 s−1, and δ = 1.5 × 10−6 cm]; C2, model inputs taken as 90% confidence limits of those suggested in the literature [e.g., KH (ClNO2) = 0.32, Φ (ClNO2)ocean = 0.5, kr = 2 × 105 s−1, and δ = 7.1 × 10−6 cm]; and C3, same as C2, with Φ (ClNO2)ocean = 0.