Figure 1. Two-step strategy used in identifying potential metastasis-driving genes in prostate cancer.
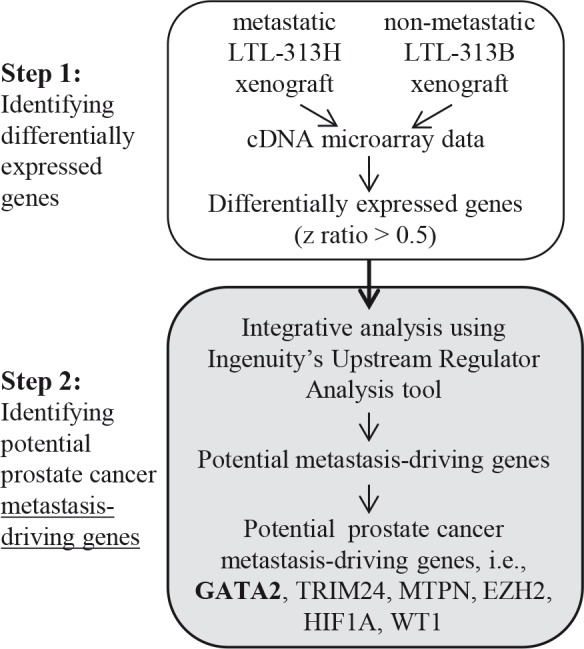
Differentially expressed genes with z ratio of > 0.5 were identified by comparing microarray gene expressions from paired metastatic LTL-313H and non-metastatic LTL-313B prostate cancer tissue xenografts. The differential gene expression profile was then analyzed using IPA's Upstream Regulator Analysis tool, in combination with reported, relevant molecular data, to predict potential metastasis-driving genes (see Supplementary Table 1). A number of potential prostate cancer metastasis-driving genes were identified including GATA2.
