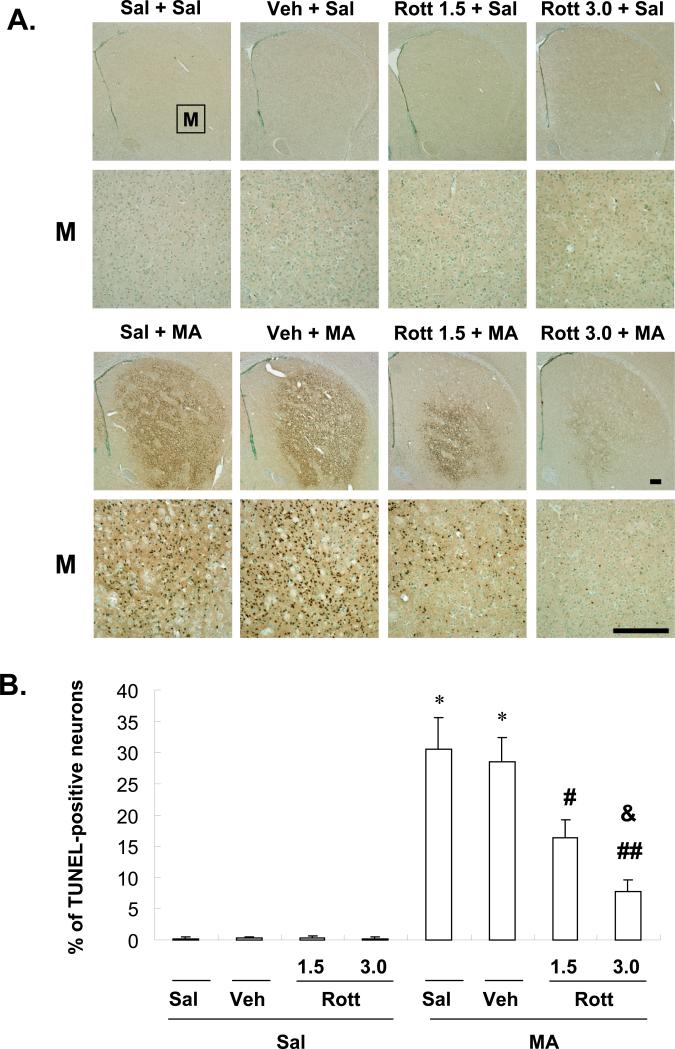
Fig. 7.
Effect of rottlerin (1.5 or 3.0 μg, i.c.v.) on methamphetamine (MA)-induced apoptosis in mice. Mice received a single injection of MA at 35 mg/kg (i.p.) and were sacrificed at 1 d after methamphetamine (MA) treatment. Representative photomicrographs of terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated dUTP nick-end labeling (TUNEL)-positive neurons in the striatum of mice treated with MA. M = magnification. Scale bar = 200 μm (A). TUNEL-positive cells were counted as described (54) (B). Sal = Saline. Vehicle (10% DMSO) = Veh. Rott 1.5 or Rott 3.0 = rottlerin, a PKCδ inhibitor at a dose of 1.5 or 3.0 μg, i.c.v.. Each value is the mean ± standard error of the mean (S.E.M.) of six animals. **P < 0.01 vs. corresponding saline-treated mice. #P < 0.05, ##P < 0.01 vs. Veh + MA-treated PKCδ (+/+) mice, &P < 0.05 vs. 1.5 μg rottlerin + MA-treated PKCδ (+/+) mice (one-way ANOVA followed by Fisher's PLSD test).