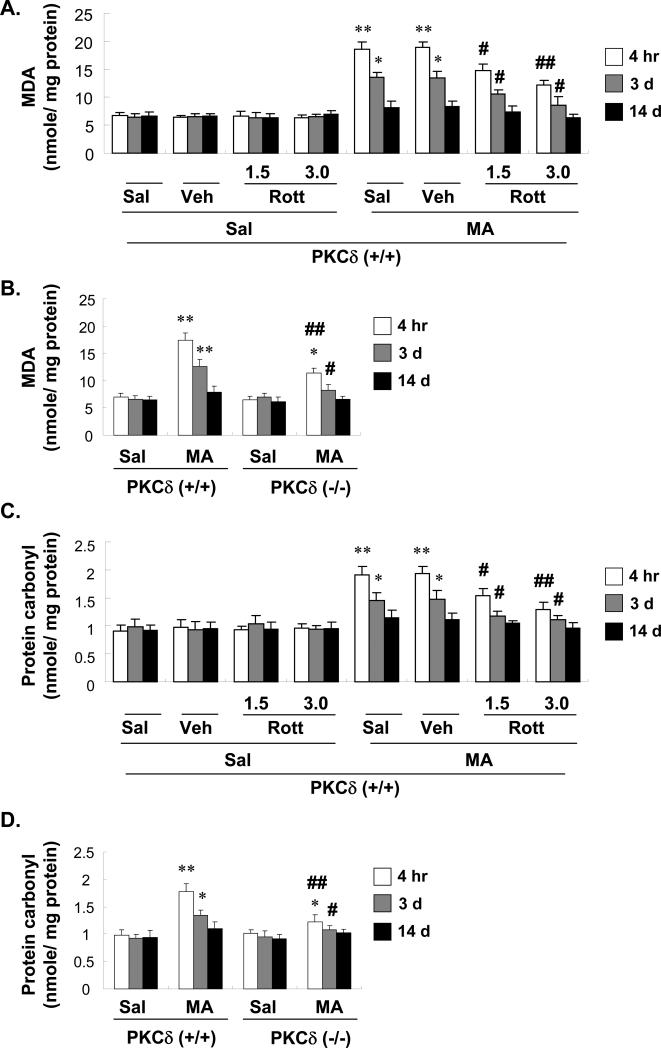
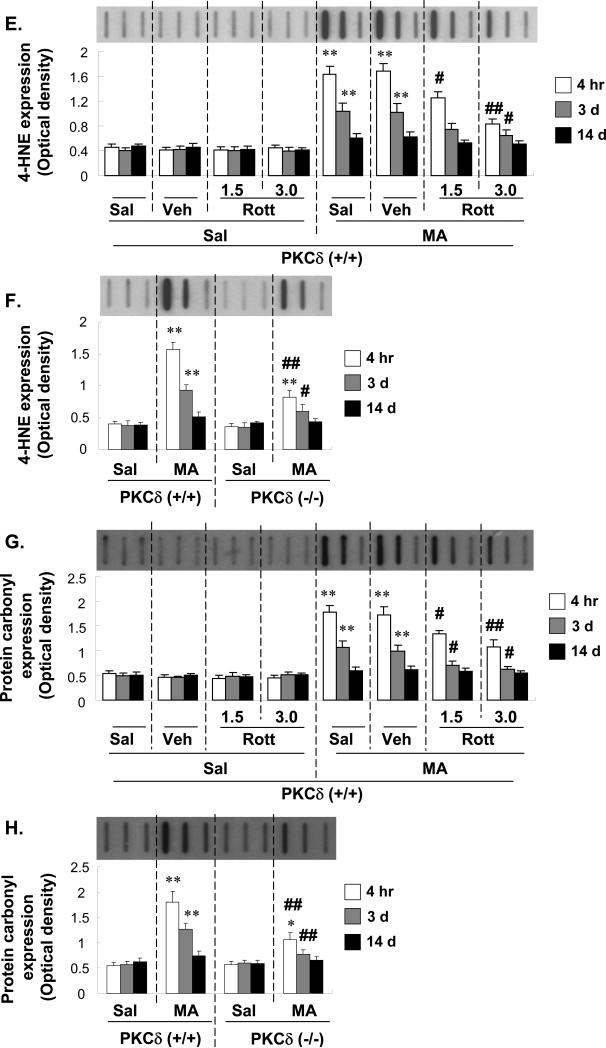
Fig. 8.
Effect of rottlerin (1.5 or 3.0 μg, i.c.v.; A, C, E, and G) or PKCδ gene knockout (B, D, F, and H) on changes in lipid peroxidation [as shown by the malondialdehyde level (A and B) and 4-HNE expression (E and F)] and protein oxidation [as shown by protein carbonyl content (C and D) and protein carbonyl expression (G and H)] in the mouse striatum at 4 h, 3 d, and 14 d after the final methamphetamine (MA) administration. Sal = Saline. Vehicle (10% DMSO) = Veh. Rott 1.5 or Rott 3.0 = rottlerin, a PKCδ inhibitor at a dose of 1.5 or 3.0 μg, i.c.v.. Each value is the mean ± standard error of the mean (S.E.M.) of 6 to 10 animals. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 vs. corresponding saline-treated mice. #P < 0.05, ##P < 0.01 vs. Veh + MA- or MA-treated PKCδ (+/+) mice (one-way ANOVA followed by Fisher's PLSD test).