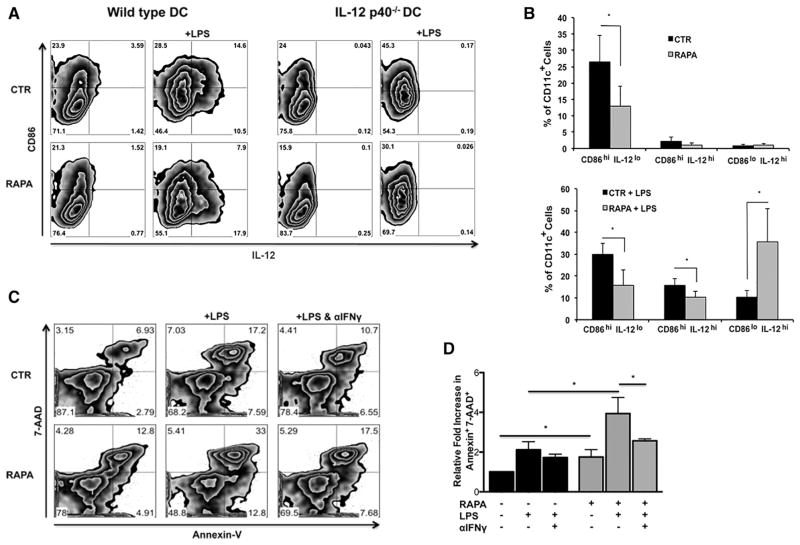
Figure 1.
LPS-stimulated RAPA-DCs express high IL-12 despite low costimulatory molecule expression and induce apoptosis of alloreactive CD4+ T cells in an IFN-γ-dependent manner. C57BL/6 (B6; H-2b) and IL-12p40−/− (B6) myeloid DCs (mDC) were generated in 7-day culture with granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor and IL-4 alone (CTR-DC) or in the presence of 10 ng/mL RAPA (RAPA-DC). CD11c-purified mDCs were incubated for 18 hours in media alone or with 100 ng/mL LPS and then analyzed for cell surface molecule expression by flow cytometry. B6 mDCs were then used in 5-day MLRs to stimulate BALB/c (H2d) CD4+ T cells. (A) RAPA-DCs, especially after LPS exposure, express low levels of CD86 and high levels of IL-12 compared with LPS-exposed CTR-DCs (CD86loIL-12hi population). IL-12p40−/− LPS-stimulated RAPA-DCs lack a high IL-12 population but have a similar CD86lo population compared with wild-type. (B) The percentage of CD86hi IL-12lo, CD86hi IL-12hi, and CD86lo IL-12hi from 7 independent experiments was averaged. Data depict mean + 1 SD. (C) Compared with CTR-DCs, especially after LPS stimulation, RAPA-DCs induced increased apoptosis (Annexin V+7-AAD+) of alloreactive CD4+ T cells (12.7% ± 2.3% versus 7.3% ± .4%; +LPS: 28.5% ± 4.4% versus 15.4% ± 2.9%; both P < .05). Blocking the activity of IFN-γ in LPS-treated RAPA-DC cultures decreased levels of apoptosis to those of LPS-treated CTR-DCs (18.7% ± 1.0% versus 15.4% ± 2.9%; NS). Plots are representative of 3 experiments performed. (D) Average fold increase in CD4+ Annexin V+ 7-AAD+ relative to CTR-DCs on day 5 of MLRs. Error bars indicate mean + 1 SD. n = 3. *P < .05.