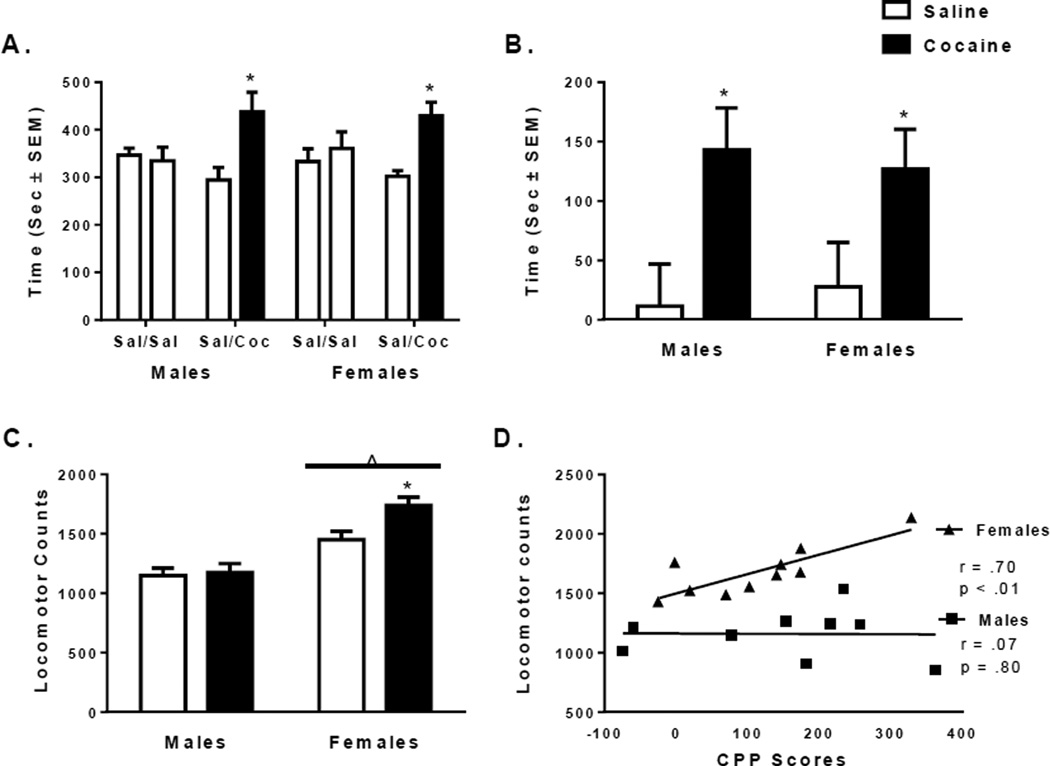
Figure 1.
CPP and locomotor responses in male and female rats during testing after conditioning with 20mg/kg cocaine. (A) Average time spent (in seconds ± SEM) in the saline paired chamber compared to the cocaine paired chamber (B) CPP scores and (C) total locomotor activity in saline (white bars) and cocaine (black bars) treated males and females (n = 8–10 rats per group). *Indicates significant difference from saline controls of the same sex at p < 0.05. ^Indicates significant main effect of sex at p < 0.05. (D) Correlation between CPP scores and total locomotor activity during the CPP test in cocaine treated male (squares) and female (triangles) rats. The Pearson Correlation coefficients and p-values are displayed within the plot.