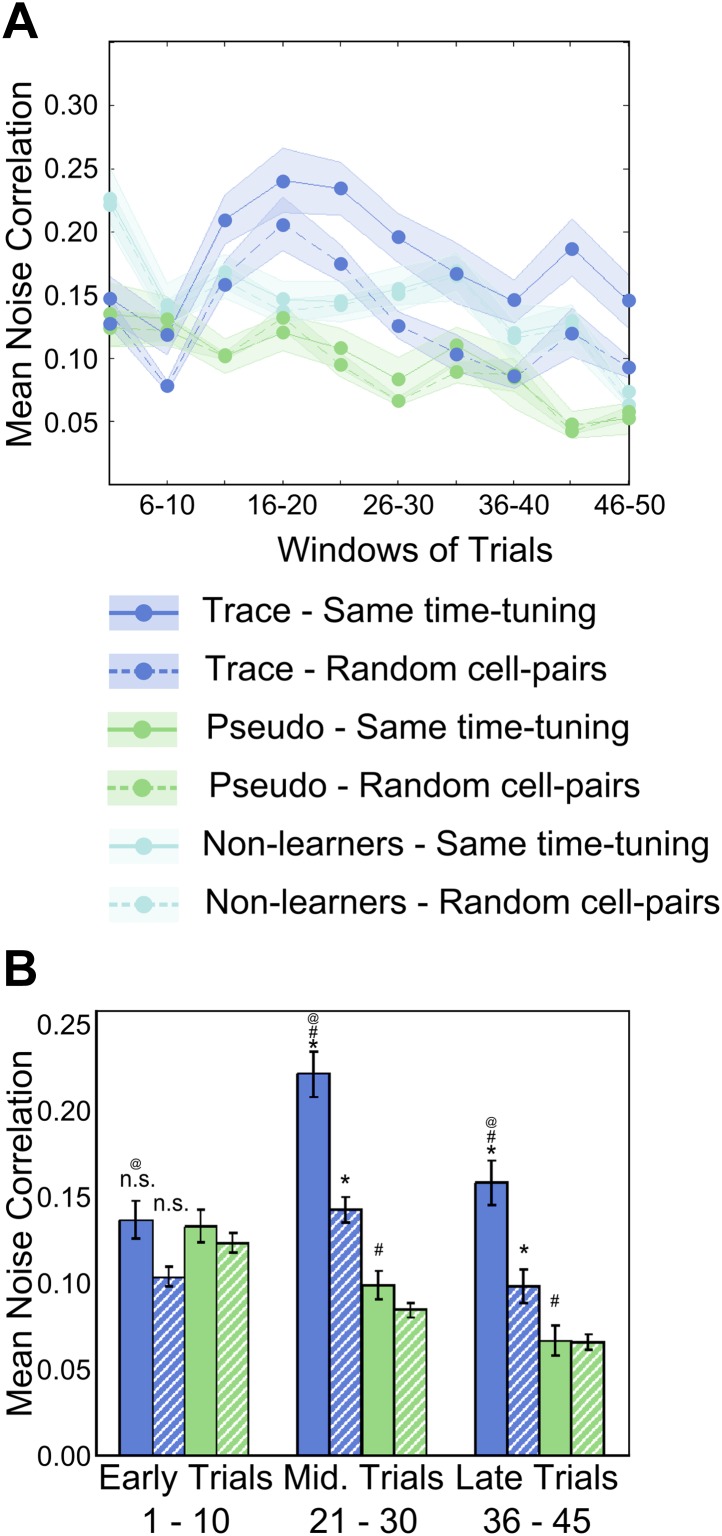
Figure 4. Area CA1 cell noise-correlations increase transiently during training.
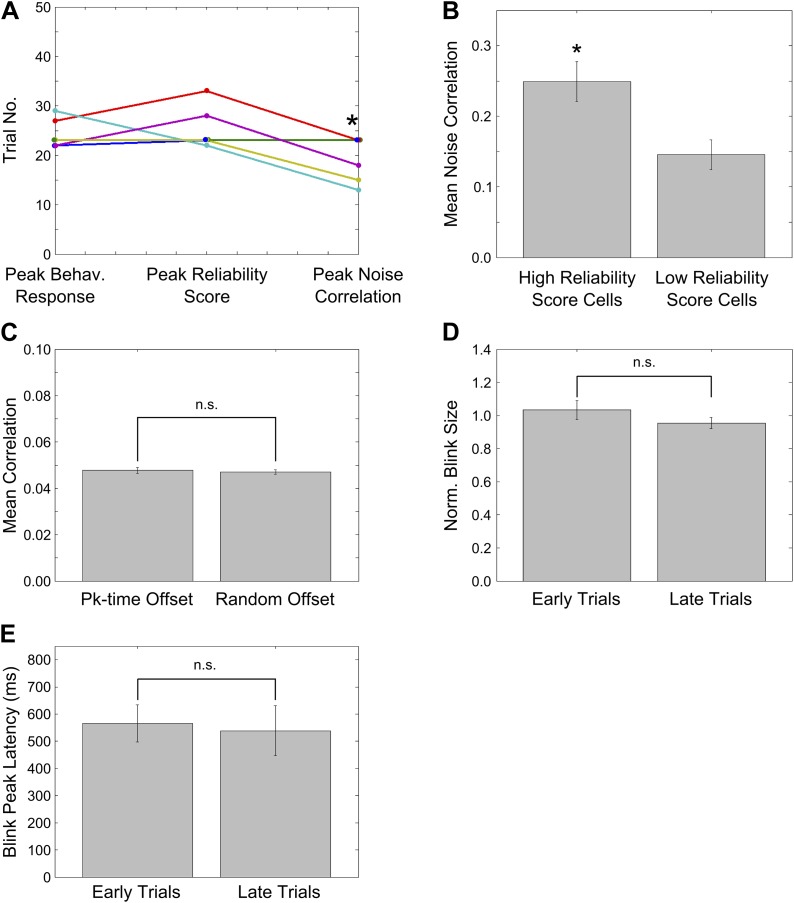
(A) Average neuron-pair noise correlations plotted as a function of training trials for task learner mice (blue curves), pseudo-conditioned mice (green curves) and non-learners (cyan curves). Solid lines represent average noise correlations between neurons that share similar time tuning (same PT), whereas dashed lines indicate average noise correlations between random neuron pairs. Pair-wise noise correlations have been determined from spontaneous activity traces over five trial windows. Shaded regions indicate SEM. (B) Summary statistics comparing average noise correlations across early (trials 1–10), middle (trials 21–30) and late (trials 36–45) stages of training, between task learner mice (blue bars) and pseudo-conditioned mice (green bars). Solid bars represent average noise correlations between neurons that share similar time tuning (same PT) whereas hatched bars represent average noise correlations between random neuron pairs. Error bars represent SEM. (* indicates within condition [same time-tuning v/s random cell-pairs], # indicates across conditions [trace learners v/s pseudo-conditioned] and @ indicates comparisons across stages of learning [early v/s middle v/s late], p<0.01; n.s. indicates not significant). Figure 4—figure supplement 1A depicts the point in the session at which behavioral CR rates, CA1 cell timing reliability and spontaneous activity correlations reach their peaks, on an individual mouse basis. It also presents further characterization of the changes in NC during learning.