Figure 6. Increased Hsp90 N-domain SUMOylation sensitizes cells to Hsp90 inhibitors.
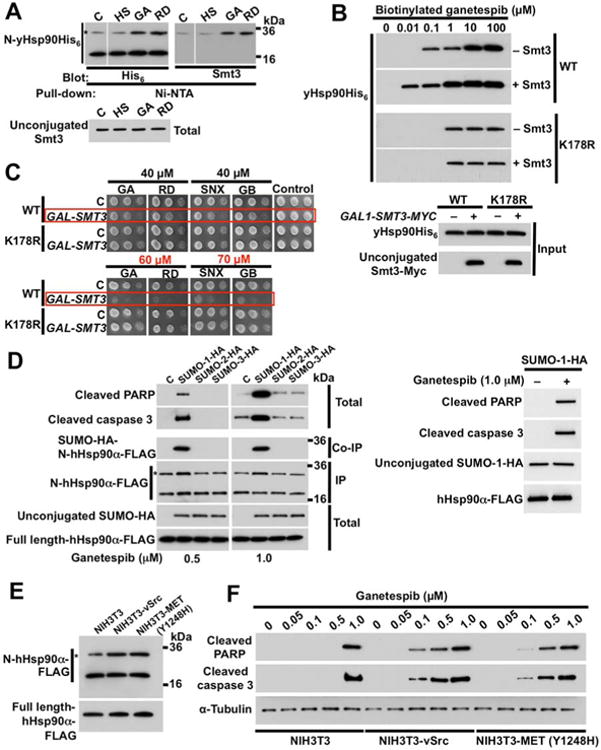
A) Effect of heat shock (HS) (40 min at 39°C), GA (50 µM, 1 h), or RD (30 µM, 1 h) on SUMOylation of yHsp90-K178 (*) was monitored by immunoblotting with anti-hexahistidine antibody. Unconjugated Smt3 was detected by anti-Smt3 antibody.
B) Yeast cells expressing wild-type yHsp90 (WT) or yHsp90-K178R (K178R), and harboring GAL1-SMT3-MYC, were grown on galactose. Hsp90 was isolated from yeast lysates by incubating with indicated amounts of biotinylated ganetespib followed by Streptavidin agarose beads, and detected by immunoblotting with anti-His6 antibody.
C) Wild-type or K178R-yHsp90-expressing yeast harboring GAL1-SMT3-MYC were grown on galactose media for 4 h. A 1:10 dilution series of 107cells/ml were spotted on YPDA agar containing indicated concentrations of the Hsp90 inhibitors GA, RD, SNX (SNX2112), or GB (ganetespib). Plates were incubated at 28°C for 4 days.
D) NIH3T3 cells were transfected with empty plasmid (C), SUMO-1-HA, SUMO-2-HA, or SUMO-3-HA. After 24 h, cells were treated with either 0.5 µM or 1.0 µM ganetespib for an additional 6 h. SUMO-1, 2 and 3, hHsp90α N-domain SUMOylation, cleaved PARP and cleaved caspase-3 were detected by immunoblotting.
E) Parental NIH3T3 cells and NIH3T3 stably expressing v-Src or constitutively active MET (Y1248H) mutant were transfected with wild-type FLAG-hHsp90α (containing a PreScission cleavage site). After 24 h, N-domain SUMOylation (*) of FLAG-hHsp90α was assessed by immunoblotting with anti-FLAG following PreScission protease digestion.
F) Parental NIH3T3 cells and NIH3T3 cells stably expressing v-Src or constitutively activated MET (Y1248H) mutant were treated with indicated amounts of ganetespib for 6h. Cleaved PARP and cleaved caspase-3 were detected by immunoblotting. α-tubulin was used as a loading control. See also Figure S5.
