Figure 2.
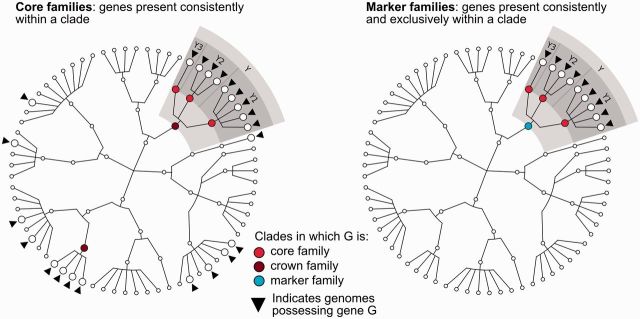
Core and marker family definitions. MetaRef defines three types of families made up of individual genes, represented here on a cartoon taxonomic tree in which leaf nodes represent strains/genomes. Core families contain genes consistently present within a clade, crown families are cores for which the clade is the lowest common ancestor, marker families are the subset of core families uniquely present only in a specific clade, and pan families comprise all genes found at least once in a sequenced microbial genome. The two trees exemplify these definitions for a gene G present in the genomes marked with a small black triangle. Specifically, on the left panel, G is a crown gene for clade Y as it is present in all its leaves and it is not a core gene in any ancestor of Y. The presence of G outside clade Y does not affect the definition of Y as a crown gene, and for clade Y1, Y2 and Y3, gene G is a core gene. On the right panel, gene G is instead a marker gene for clade Y as G is never present in genomes outside clade Y.
