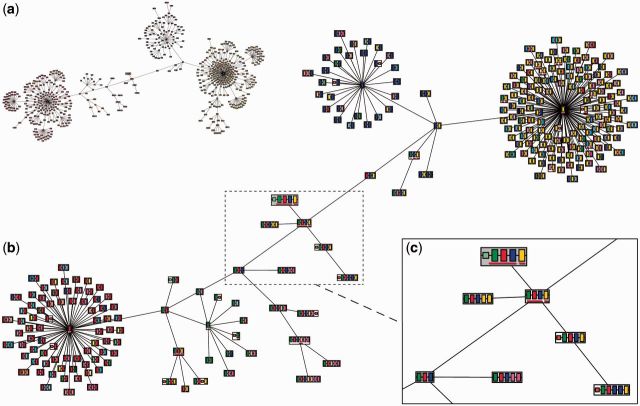
Figure 2.
An ArchSchema domain architecture network for coagulation factor Xa from Homo sapiens, PDB entry 2p16. (a) The initial network shows 622 domain architectures (i.e. sequences of Pfam domains), each represented by a different node on the graph. There are over 5500 domain architecture with one of more domains in common with that of coagulation factor Xa, but the graph is automatically trimmed to show only the closest relatives. (b) The same graph, but trimmed via the ArchSchema controls to remove the more distant nodes. (c) A blow-up of the central section of the trimmed graph. Here one can see the sequences of individual Pfam domains, as depicted by the coloured boxes inside each node—taller boxes corresponding to Pfam-A domains and smaller ones to Pfam-B. The node representing coagulation factor Xa is the slightly larger box with a grey background at the top of the inset. Red lines underneath domains indicate there is at least one entry containing the domain in the PDB. (Clicking on the node and then on the proteins marked with a green tick takes you to the structures). Satellite nodes can be added to the plots by selecting the type required: UniProtKB sequence identifiers, PDB identifiers or enzyme classes.