Abstract
Cucumis sativus L. seeds and 5-day-old dark-grown cotyledons contain 25 and 18 S cytoplasmic ribosomal RNAs as main components. The major increase in nucleic acid content in both green and etiolated cotyledons occurs between days 5 and 7 of germination. This increase is characterized by an important synthesis of 23 and 16 S plastid (chloroplast and proplastid) ribosomal RNAs. Proplastid RNA synthesis appears to continue for a longer period in the dark-grown cotyledons, despite a total RNA content considerably less than in the light-grown cotyledons.
The nonribosomal distribution of the chloroplast and proplastid ribosomal RNAs observed in all cases (after extraction and fractionation) results from the lability of the 23 S component. This degradation increases if the chloroplasts and proplastids are isolated prior to extraction of their nucleic acid.
Full text
PDF
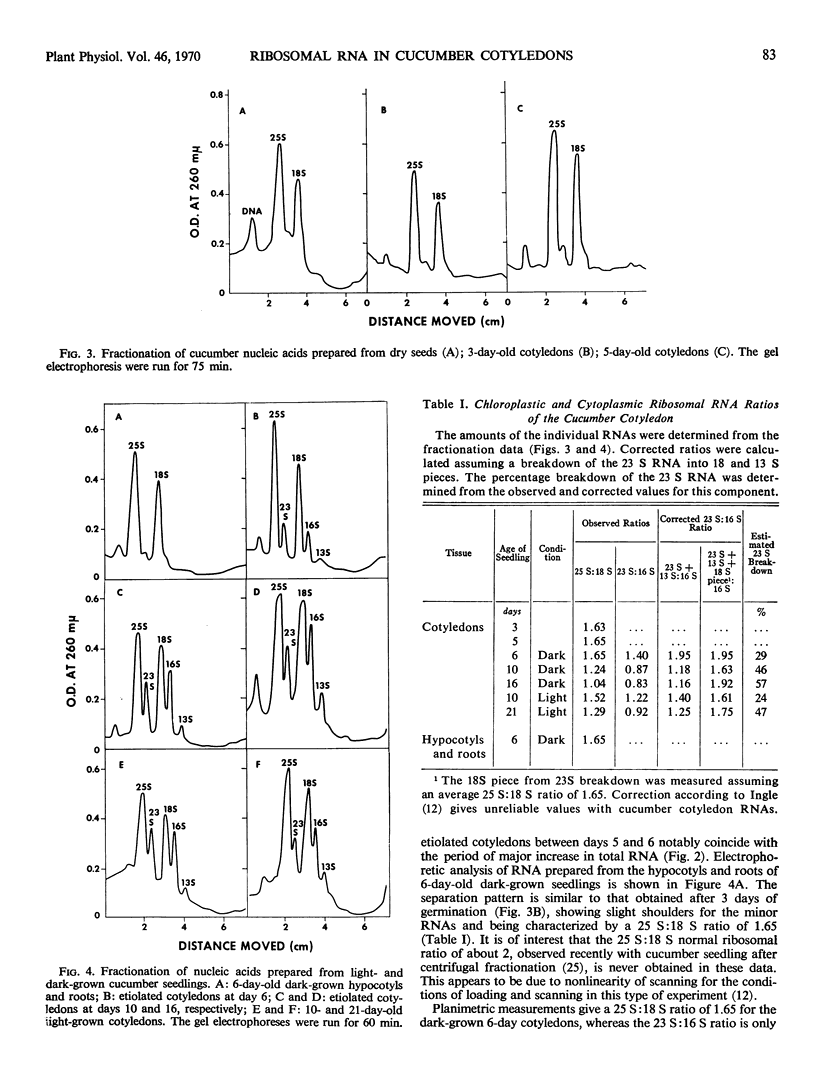
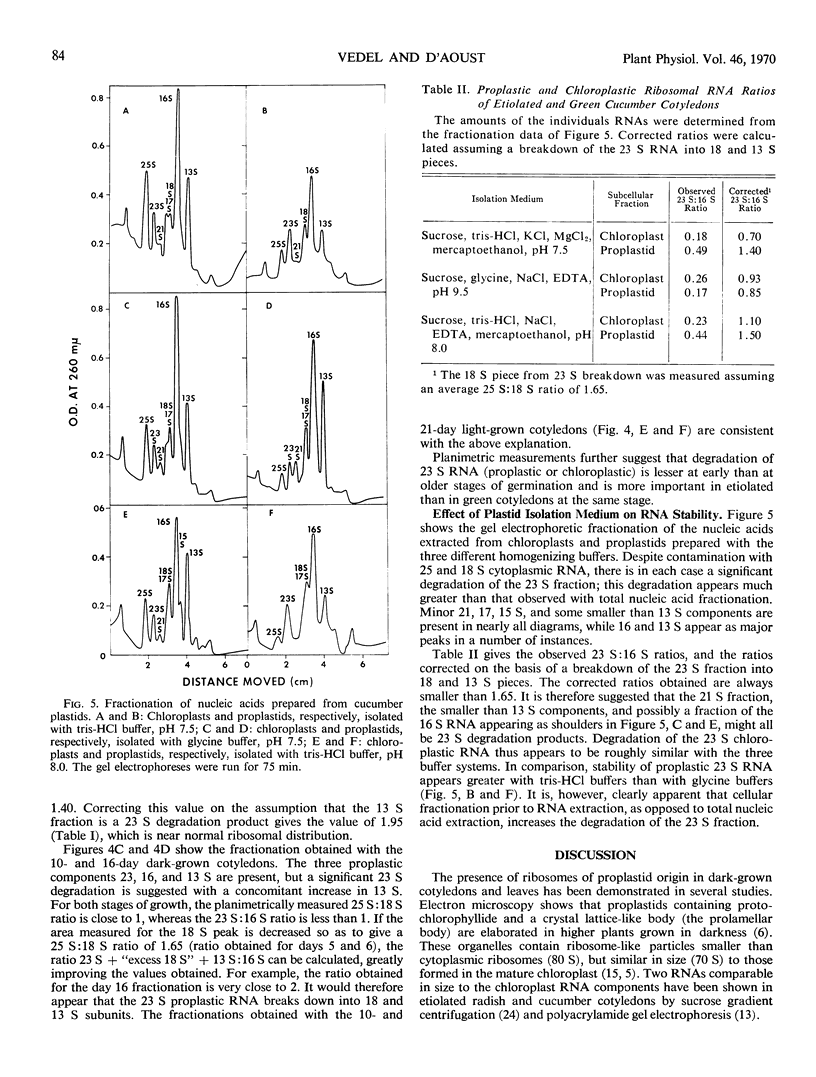

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bagi G., Farkas G. L. A new aspect of the anti-stress effect of kinetin. Experientia. 1968 Apr 15;24(4):397–398. doi: 10.1007/BF02140843. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bard S. A., Gordon M. P. Studies on spinach chloroplast and nuclear DNA using large-scale tissue preparations. Plant Physiol. 1969 Mar;44(3):377–384. doi: 10.1104/pp.44.3.377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop D. H., Claybrook J. R., Spiegelman S. Electrophoretic separation of viral nucleic acids on polyacrylamide gels. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jun 28;26(3):373–387. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90310-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boardman N. K. Ribosome composition and chloroplast development in Phaseolus vulgaris. Exp Cell Res. 1966 Sep;43(2):474–482. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(66)90074-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Click R. E., Hackett D. P. The isolation of ribonucleic acid from plant, bacterial or animal cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Oct 24;129(1):74–84. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(66)90010-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farkas G. L., Stahmann M. A. On the nature of changes in peroxidase isoenzymes in bean leaves infected by southern bean mosaic virus. Phytopathology. 1966 Jun;56(6):669–677. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gyldenholm A. O. Macromolecular physiology of plastids V. On the nucleic acid metabolism during chloroplast development. Hereditas. 1968;59(1):142–168. doi: 10.1111/j.1601-5223.1968.tb02168.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsiao T. C. Ribonuclease Activity Associated With Ribosomes of Zea mays. Plant Physiol. 1968 Sep;43(9):1355–1361. doi: 10.1104/pp.43.9.1355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingle J. Synthesis and Stability of Chloroplast Ribosomal-RNA's. Plant Physiol. 1968 Sep;43(9):1448–1454. doi: 10.1104/pp.43.9.1448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingle J. The effect of light and inhibitors on chloroplast and cytoplasmic RNA synthesis. Plant Physiol. 1968 Nov;43(11):1850–1854. doi: 10.1104/pp.43.11.1850. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson A. B. A procedure for isolation of proplastids from etiolated maize leaves. J Cell Biol. 1968 Jul;38(1):238–244. doi: 10.1083/jcb.38.1.238. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson A. B., Swift H., Bogorad L. Cytochemical studies concerning the occurrence and distribution of RNA in plastids of Zea mays. J Cell Biol. 1963 Jun;17:557–570. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.3.557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loening U. E., Ingle J. Diversity of RNA components in green plant tissues. Nature. 1967 Jul 22;215(5099):363–367. doi: 10.1038/215363a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loening U. E. Molecular weights of ribosomal RNA in relation to evolution. J Mol Biol. 1968 Dec;38(3):355–365. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90391-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loening U. E. The fractionation of high-molecular-weight ribonucleic acid by polyacrylamide-gel electrophoresis. Biochem J. 1967 Jan;102(1):251–257. doi: 10.1042/bj1020251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddi K. K. Ribonuclease induction in cells transformed by Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Oct;56(4):1207–1214. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.4.1207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SPENCER D., WILDMAN S. G. THE INCORPORATION OF AMINO ACIDS INTO PROTEIN BY CELL-FREE EXTRACTS FROM TOBACCO LEAVES. Biochemistry. 1964 Jul;3:954–959. doi: 10.1021/bi00895a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stutz E., Noll H. Characterization of cytoplasmic and chloroplast polysomes in plants: evidence for three classes of ribosomal RNA in nature. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Mar;57(3):774–781. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.3.774. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tewari K. K., Wildman S. G. Function of chloroplast DNA. I. Hybridization studies involving nuclear and chloroplast DNA with RNA from cytoplasmic (80S) and chloroplast (70S) ribosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Feb;59(2):569–576. doi: 10.1073/pnas.59.2.569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vedel F., D'Aoust M. J. Rapid separation of ribosomal RNA by sucrose density gradient centrifugation with a fixed-angle rotor. Anal Biochem. 1970 May;35(1):54–59. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(70)90008-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



