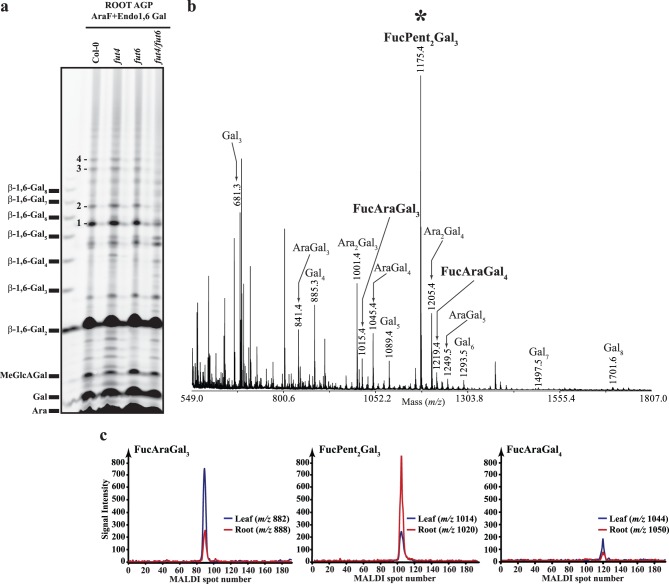
Figure 4. Characterisation of oligosaccharides released by the sequential digestion with the AG-specific enzymes α-arabinofuranosidase and endo-β-(1→6)-galactanase from Arabidopsis root AGP extracts.
(a) Polysaccharide Analysis using Carbohydrate gel Electrophoresis (PACE). Oligosaccharide products from wild-type (Col-0), fut4, fut6 and fut4/fut6 were reductively aminated with 2-aminonaphthaline trisulfonic acid and separated by electrophoresis on acrylamide gels. An oligosaccharide ladder prepared from β-(1→6)-galactan was used as migration marker. The numbers indicate putatively fucosylated oligosaccharides with altered abundance in the wild-type and fut mutant samples. (b) MALDI-ToF-MS spectrum of per-methylated oligosaccharide products from wild-type plants. Peaks marked with an asterisk (*) were selected for high-energy MALDI-CID structural analysis. (c) Extracted ion chromatograms (EICs) for the fucosylated oligosaccharides originating from Arabidopsis leaf (blue lines) and root (red lines) AGP extracts hydrolysed sequentially by α-arabinofuranosidase, exo-β-(1→3)-galactanase, β-glucuronidase and endo-β-(1→6)-galactanase. Arabidopsis root AGP extracts contain the same three fucosylated oligosaccharides as leaves albeit in different relative abundances.