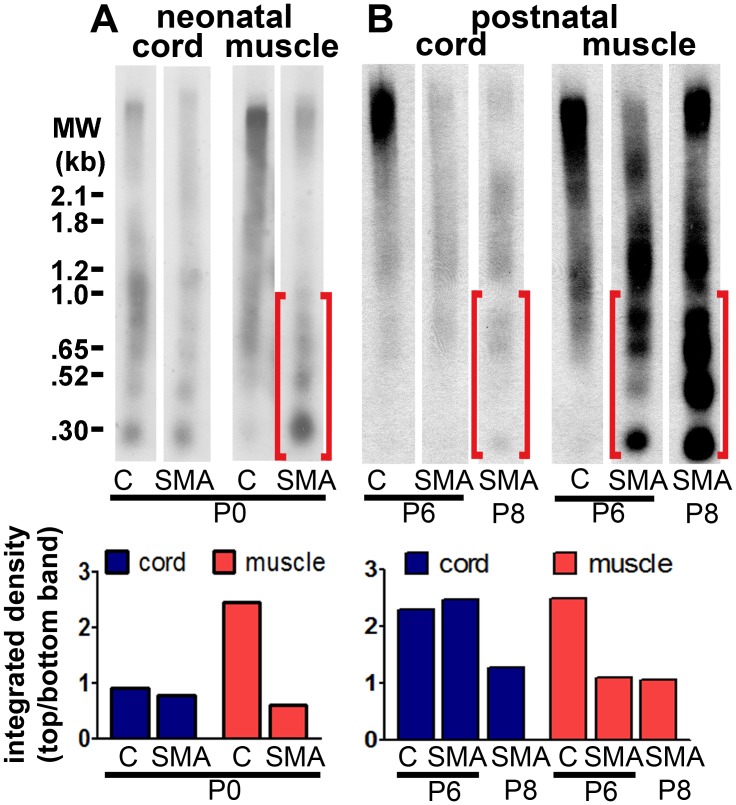
Figure 4. Internucleosomal fragmentation of DNA emerges in skeletal muscle before spinal cord in SMA mice.
Whole genomic DNA from spinal cord and hind limb muscle (postnatal days P0–P8) was separated by gel electrophoresis. DNA breaks were end-labeled with DIG-dUTP by TdT and detected using a DIG-based Southern blot. A DIG-conjugated molecular weight ladder was run on the same gel (size marked on the left). Brackets show areas of lower molecular weight DNA in skeletal muscle, indicating DNA fragmentation. Substantial differences in internucleosomal fragmentation of DNA were not observed between control and SMA spinal cord until postnatal day 8. Bar graphs under each blot represent integrated density measurements of the top band in each lane divided by the bottom band in each lane. A. Southern blot of spinal cord and skeletal muscle DNA from SMA and control (“C”) littermates at postnatal day 0. B. Southern blot of spinal cord and skeletal muscle DNA from SMA and control (“C”) littermates at postnatal day 6 and a separate SMA mouse at postnatal day 8.