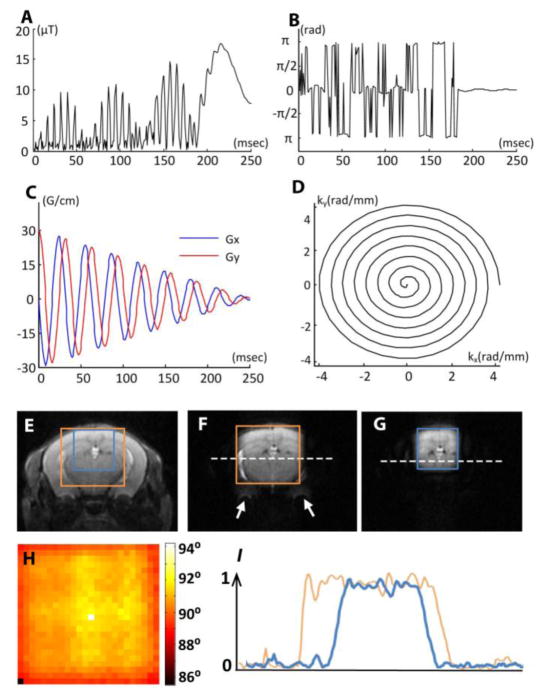
Figure 1.
Spatially selective excitation RF pulse and its experimental validation. A–B: The pulse amplitude and phase of a typical 90° selective excitation pulse. C–D: an eight-turn spiral-in gradient waveform and excitation k-space trajectory in the x-y plane. The gradient waveform was synchronized with the RF waveform to achieve selective excitation. (E) A T2-weighted image of an adult mouse brain overlaid with a 8 mm x 8 mm field of excitation (FOE) (orange) and a 6 mm x 6 mm FOE (blue). (F–G) The results of selective excitation corresponding to the 8 mm x 8 mm and 6 mm x 6 mm FOEs shown in (E), respectively. H: the measured flip angle map of the excited region (corresponding to the FOE in F). I: the normalized (with respect to the maximal value) intensity profiles along the dashed lines in F and G.