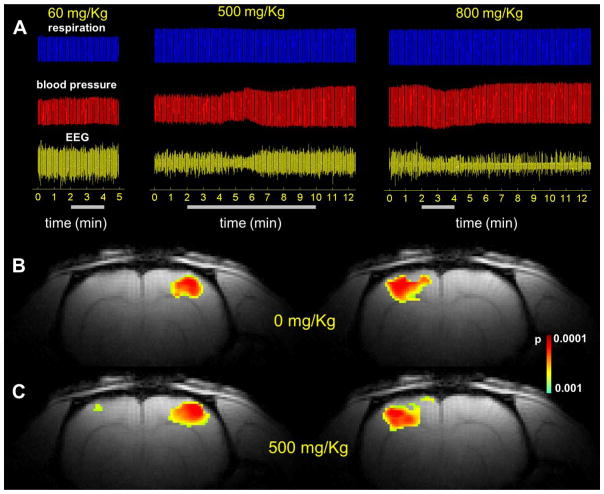
Figure 3. Effect of various FDG doses on animal physiology.
Measurements of respiration (A, top), blood pressure (A, middle) and EEG (A, bottom) show minimum effects of FDG for doses up to 500 mg/Kg, while doses higher than 500 mg/Kg result in adverse effects on physiology, monitored by EEG signal. Left and right forepaw stimulations (2 mA, 0.3ms, 3Hz) before (B) and after infusion of 500 mg/Kg FDG (C). The results show that the activated areas before and after FDG infusion are very similar, which indicates that the brain activity is not affected by the infusion of 500 mg/Kg FDG. The FDG total dose is indicated in each case at the top of the respiration signal, while the bars below the EEG signal represent the duration of the FDG infusion.