Fig. 2.
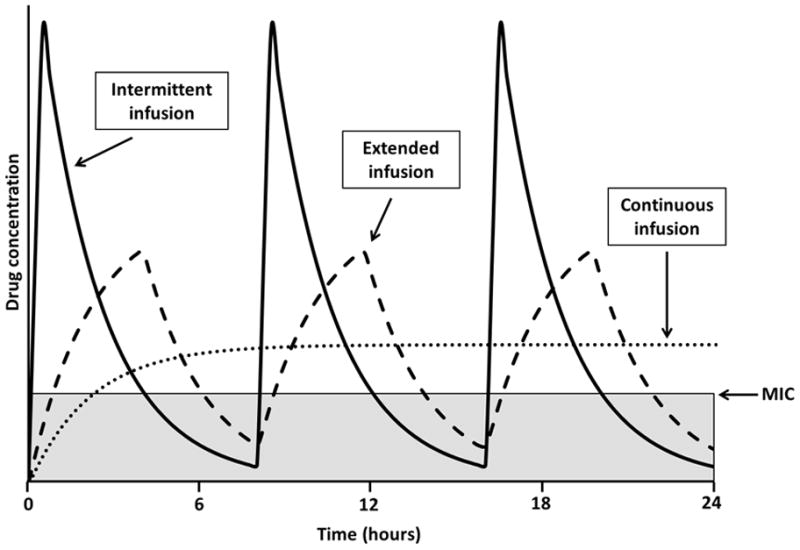
Time above the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) for intermittent, extended and continuous infusion of time-dependent drugs. Extended or continuous infusion of time-dependent drugs can improve the percentage of the dosing interval above the MIC (T>MIC), particularly when treating infections with elevated MICs. Intermittent infusion (solid line), extended infusion (dashed line) and continuous infusion (dotted line) are compared with the time that each dosing regimen is below the MIC, highlighted by the grey area. Curves were generated using the same total daily dose and consistent pharmacokinetic parameters for each regimen.
