Figure 6.
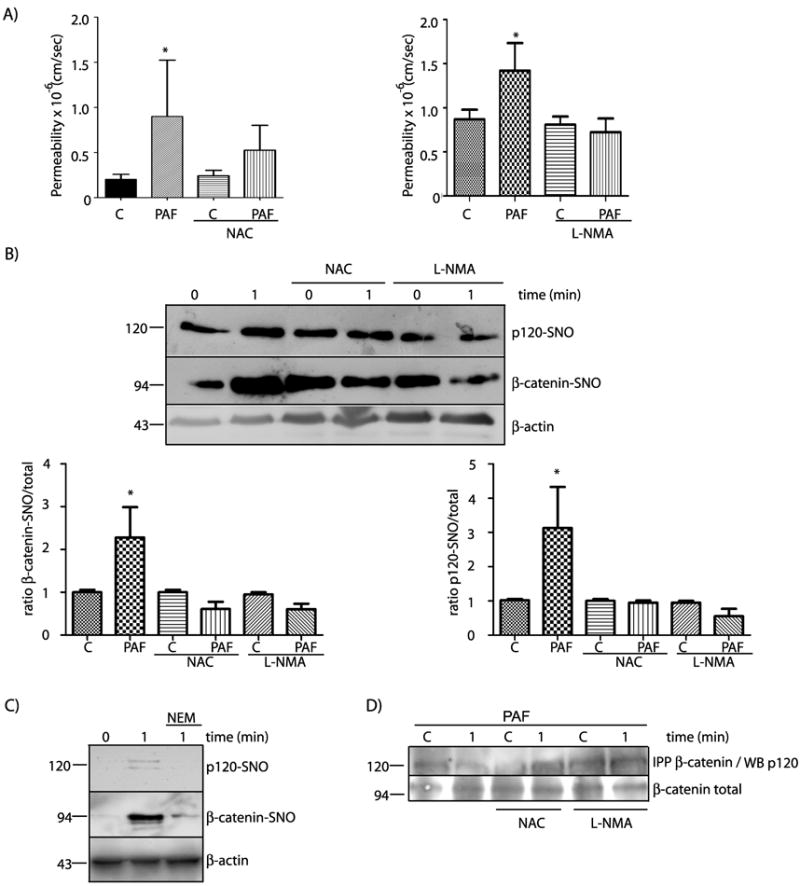
PAF-induced hyperpermeability to macromolecules correlates strongly with SNO of β-catenin and p120 in EAhy926 cells. A) PAF-induced hyperpermeability in EAhy926 cells is blocked by inhibition of SNO with NAC (left side) and by inhibition of eNOS with L-NMA (right side). C= control. Data are expressed as mean permeability ± SEM. * P < 0.05 relative to control, n = 3. B) PAF-induced SNO of β-catenin and p120 is prevented by NAC, a competitive inhibitor of SNO, and by L-NMA, an inhibitor of eNOS. * P < 0.05 as compared with control; n =3. C) PAF-induced SNO of β-catenin and p120 is prevented by NEM, a blocker of SH groups. D) Protein extracts from EAhy926 cells treated with 10-7 moles/L PAF for 1 minute, in the presence of NAC or L-NMA, were immunoprecipitated for β-catenin and probed by Western blot with anti-p120 antibodies. The representative blot shows that NAC and L-NMA blocked PAF-induced disruption of the association between β-catenin and p120.
