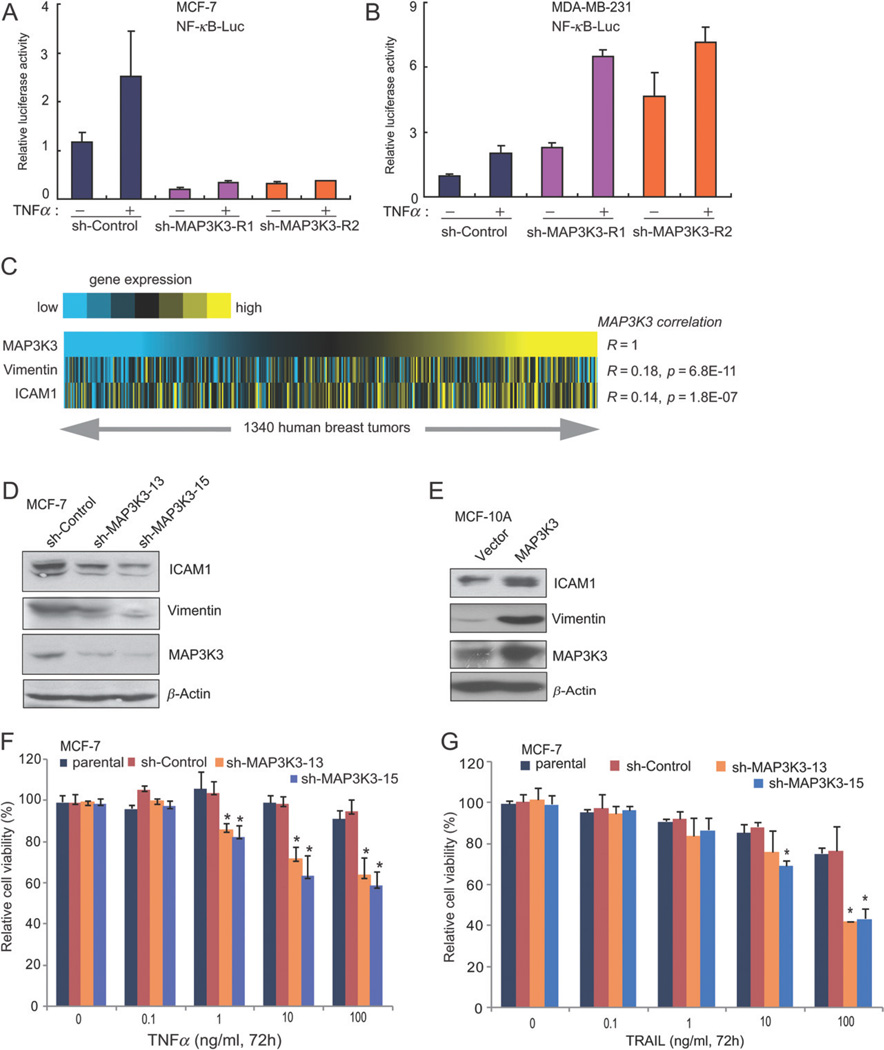
Figure 4.
MAP3K3 regulates NF-κB targets and knockdown of MAP3K3 expression enhances TNFα- and TRAIL-induced apoptosis in MCF-7 cells. (A) Knockdown of MAP3K3 expression in MCF-7 cells inhibited basal and TNFα-induced NF-κB activity. NF-κB-dependent luciferase reporter and control Renilla luciferase reporter vectors were transfected into control and sh-MAP3K3 MCF-7 cells; 36 h after transfection, cells were left untreated or treated with TNFα for 16 h before luciferase reporter assays were performed. (B) The effect of knockdown MAP3K3 expression on NF-κB activity in MDA-MB-231 cells. (C) Heat map showing positive correlation of ICAM1 and Vimentin expression with MAP3K3 expression across 1340 breast tumours (yellow, high expression; R, Spearman’s correlation). (D) Immunoblotting analysis showing decreased levels of ICAM1 and Vimentin in MCF-7 cells with MAP3K3 knockdown. (E) Immunoblotting analysis showing the increased levels of ICAM1 and Vimentin in MCF-10A cells stably over-expressing MAP3K3. Results from (D, E) are representative of three independent experiments. (F, G) Quantification of cell numbers (by CCK-8) in cell cultures treated with the indicated concentrations of TNFα (F) or TRAIL (G). Error bars represent SEM from three independent experiments.