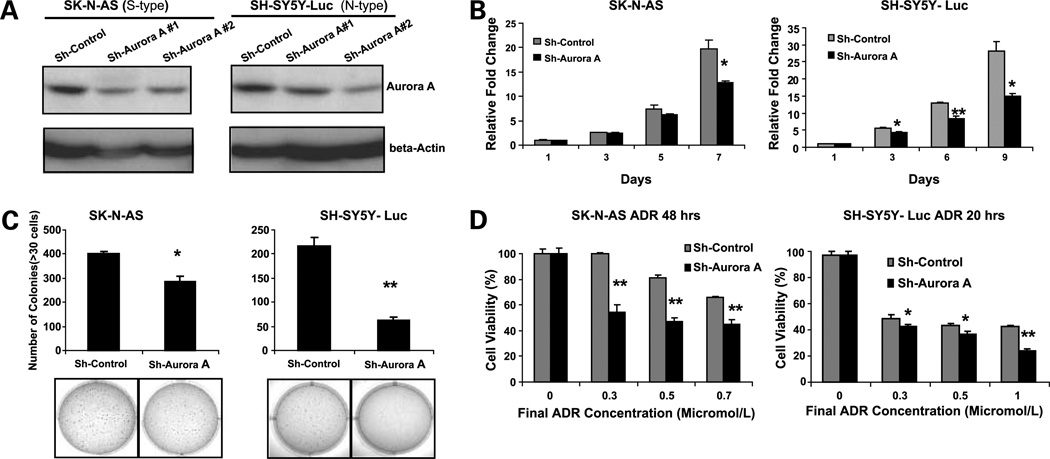
Figure 3.
Inhibition of Aurora A expression causes a proliferation defect and enhances chemosensitivity in both S-type and N-type human neuroblastoma cell lines. Aurora A expression in S-type SK-N-AS and N-type SH-SY5Y-Luc cells stably transduced with pSR-Sh-scramble control and pSR-Sh-Aurora A (#1 and #2 sequence). A, cells were analyzed by Western blot after 10 d of puromycin (2 µg/mL) selection. B, inhibition of Aurora A expression causes a proliferation defect. The SK-N-AS and SH-SY5Y-Luc Sh-Control and Sh-Aurora A #2 cell lines were plated in 96-well plates at 1 × 103 cells per well. The Cell Counting Kit-8 tetrazolium salt–based proliferation assay was used to quantify cellular proliferation relative to day 1 absorbance measured at 450 nm. These experiments were done in triplicate and reported as mean ± SD. C, SK-N-AS and SH-SY5Y-Luc Sh-Control and Sh-Aurora A #2 stably transduced cell lines were plated in 0.3% agarose/DMEM on top of a 0.5% agarose/DMEM layer. After 14 d of growth, colonies were stained with MTT (bottom) and colonies >30 cells were counted (top). A similar result was observed using Sh-Aurora A #1 cells (data not shown). D, inhibition of Aurora A expression increases chemosensitivity. SK-N-AS and SH-SY5Y-Luc Sh-Control and Sh-Aurora A #2 cell lines were plated in 96-well plates at 1 × 104 cells per well. After 24 h of growth, all of the cell lines were treated with the indicated micromolar concentration of doxorubicin for the indicated amount of time. Cell viability was determined with the Cell Counting Kit-8 cell viability assay relative to the 0 µmol/L group. All experiments were done in triplicate and statistical significance was determined by Student's t test where P < 0.05 was statistically significant. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.001 compared with the Sh-Control group.