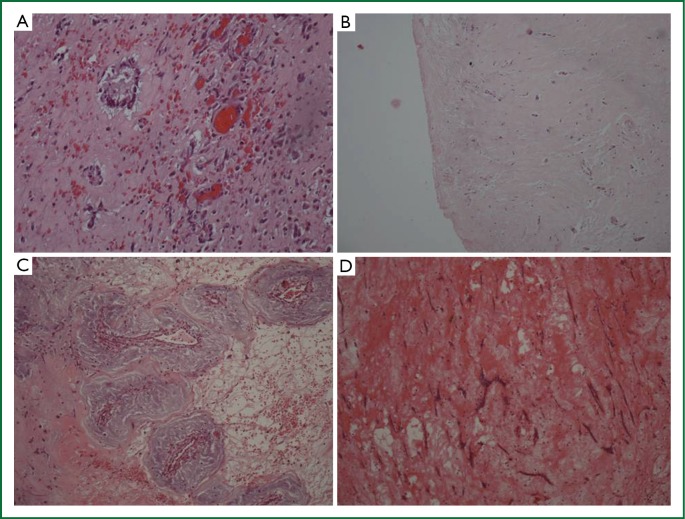
Figure 6.
Histologic characteristics of myxomas. (A) Active myxoma with normal differentiation. Increased cellularity of myxoma cells, which form rudimentary vascular structures, (Haematoxylin-eosin ×200); (B) Mildly active myxoma with medium differentiation—Variable cellularity of myxoma cells that form vascular structures, (Haematoxylin-eosin ×200); (C) Inactive myxoma with normal differentiation—Low cellularity of myxoma cells, which form rudimentary vascular structures, (Haematoxylin-eosin ×200); (D) Inactive myxoma with poor differentiation—Low cellularity of myxoma cells, dispersed or lepodic, which form short chains, (Haematoxylin-eosin ×200).