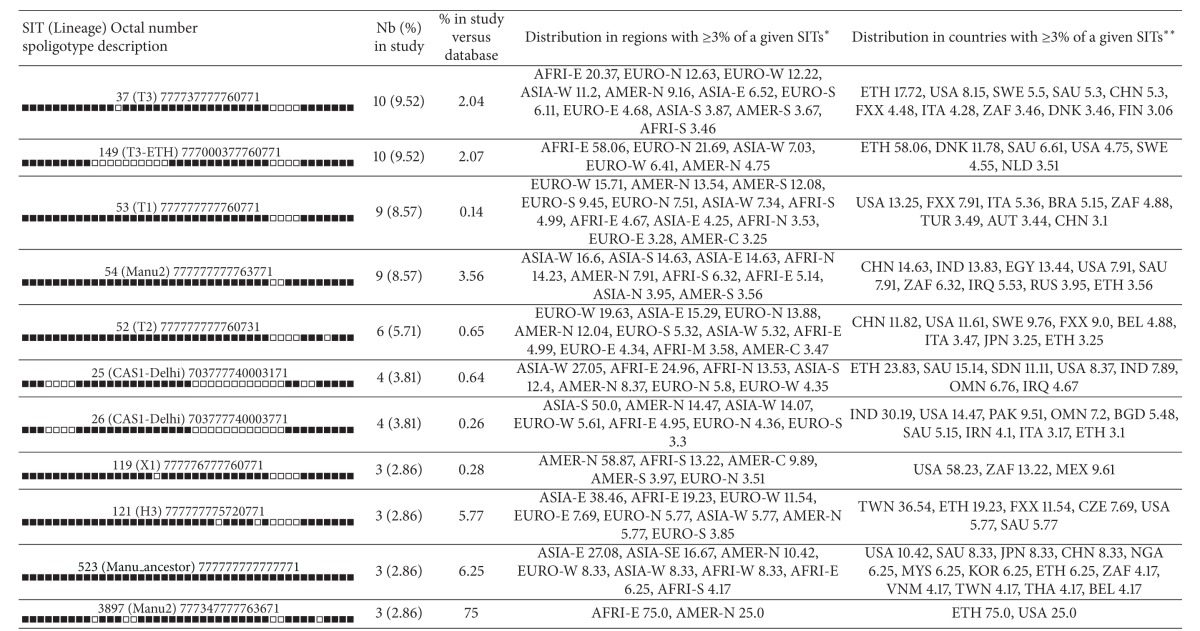
Table 3.
Description of clusters containing 3 or more isolates in this study and their worldwide distribution in the SITVIT2 database.
|
*Worldwide distribution (analysis made on August 18, 2013) is reported for regions with more than 3% of given SITs as compared to their total number in the SITVIT2 database. The definition of macrogeographical regions and subregions (http://unstats.un.org/unsd/methods/m49/m49regin.htm) is according to the United Nations; regions: AFRI (Africa), AMER (Americas), ASIA (Asia), EURO (Europe), and OCE (Oceania), subdivided in: E (Eastern), M (Middle), C (Central), N (Northern), S (Southern), SE (South-Eastern), and W (Western). Furthermore, CARIB (Caribbean) belongs to Americas, while Oceania is subdivided in 4 subregions, AUST (Australasia), MEL (Melanesia), MIC (Micronesia), and POLY (Polynesia). Note that in our classification scheme, Russia has been attributed a new subregion by itself (Northern Asia) instead of including it among the rest of Eastern Europe. It reflects its geographical localization as well as due to the similarity of specific TB genotypes circulating in Russia (a majority of Beijing genotypes) with those prevalent in Central, Eastern, and Southeastern Asia.
**The 3-letter country codes are according to http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ISO_3166-1_alpha-3; countrywide distribution is only shown for SITs with ≥3% of given SITs as compared to their total number in the SITVIT2 database.
