Figure.
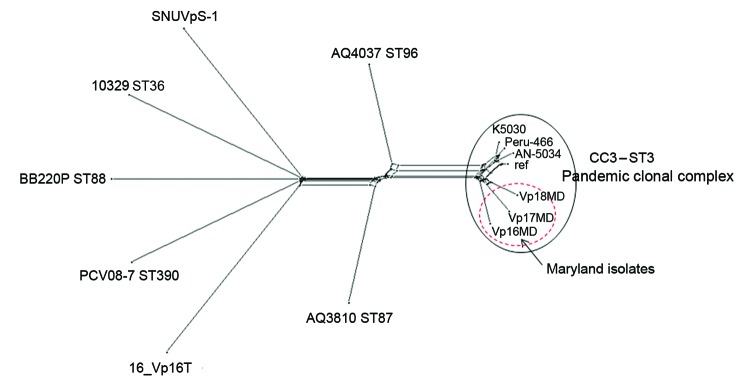
Neighbor-Net graph generated with the Bacterial Isolate Genome Sequence Database genome (BIGSdb) comparator tool implemented within the Vibrio parahaemolyticus MLST database (http://pubmlst.org/vparahaemolyticus) (7,8) using 2,613 variable loci. These loci were identified by using as a reference (ref) the V. parahaemolyticus strain RIMD2210633 chromosome I (3,080 genes) and conducting a whole-genome MLST (wgMLST) for V. parahaemolyticus genomes available through GenBank (AN-5034 O4:K68 ST3, Peru-466 ST3, K5030 ST3, 16_VP16T, AQ3810 ST87, AQ4037 ST96, PCV08–7 ST390, BB220P ST88, and SNUVpS-1) and 3 Maryland outbreak strains (Vp16MD, Vp17MD, and Vp18MD). This typing showed that these 3 strains belonged to the pandemic CC3. A similar graph was obtained by using chromosome II of the same strain as reference (data not shown). In brief, the BIGSdb genome comparator tool performs wgMLST, which produces a color-coded wgMLST output (Technical Appendix 2) that facilitates comparison among isolates. This loci output is further categorized into loci that are 1) variable among all isolates, 2) identical among all isolates, 3) missing in all isolates, and 4) incomplete because of being located at the ends of contigs. The variable loci among all isolates are the loci used for assessing relationships and producing a distance matrix based on the number of variable alleles; the strains are resolved into a network by using the NeighborNet algorithm (9). MLST, multilocus sequence typing; CC, clonal complex; ST, sequence type.
